Identification and Characterization of EvpQ, a Novel T6SS Effector Encoded on a Mobile Genetic Element in Edwardsiella piscicida
- PMID: 33776977
- PMCID: PMC7991086
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.643498
Identification and Characterization of EvpQ, a Novel T6SS Effector Encoded on a Mobile Genetic Element in Edwardsiella piscicida
Abstract
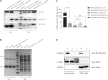
In this study, a hypothetical protein (ORF02740) secreted by Edwardsiella piscicida was identified. We renamed the ORF02740 protein as EvpQ, which is encoded by a mobile genetic element (MGE) in E. piscicida genome. The evpQ gene is spaced by 513 genes from type VI secretion system (T6SS) gene cluster. Low GC content, three tRNA, and three transposase genes nearby evpQ define this MGE that evpQ localizes as a genomic island. Sequence analysis reveals that EvpQ shares a conserved domain of C70 family cysteine protease and shares 23.91% identity with T3SS effector AvrRpt2 of phytopathogenic Erwinia amylovora. Instead, EvpQ of E. piscicida is proved to be secreted at a T6SS-dependent manner, and it can be translocated into host cells. EvpQ is thereof a novel T6SS effector. Significantly decreased competitive index of ΔevpQ strain in blue gourami fish (0.53 ± 0.27 in head kidney and 0.44 ± 0.19 in spleen) indicates that EvpQ contributes to the pathogenesis of E. piscicida. At 8-, 18-, and 24-h post-subculture into DMEM, the transcription of evpQ was found to be negatively regulated by Fur and positively regulated by EsrC, and the steady-state protein levels of EvpQ are negatively controlled by RpoS. Our study lays a foundation for further understanding the pathogenic role of T6SS in edwardsiellosis.
Keywords: Edwardsiella piscicida; EvpQ; effector; mobile genetic element; regulation; type VI secretion system.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Liu, Liao, He, Sun, Nie and Xie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


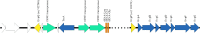


References
-
- Chakraborty S., Sivaraman J., Leung K. Y., Mok Y. K. (2011). Two-component PhoB-PhoR regulatory system and ferric uptake regulator sense phosphate and iron to control virulence genes in type III and VI secretion systems of Edwardsiella tarda. J. Biol. Chem. 286 39417–39430. 10.1074/jbc.m111.295188 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

