Value Analysis of Using Urinary Microalbumin in Artificial Intelligence Medical Institutions to Detect Early Renal Damage in Diabetes
- PMID: 33777345
- PMCID: PMC7979295
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6678454
Value Analysis of Using Urinary Microalbumin in Artificial Intelligence Medical Institutions to Detect Early Renal Damage in Diabetes
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Value Analysis of Using Urinary Microalbumin in Artificial Intelligence Medical Institutions to Detect Early Renal Damage in Diabetes.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Nov 17;2022:9871586. doi: 10.1155/2022/9871586. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. PMID: 36437816 Free PMC article.
Abstract
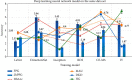
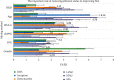
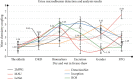
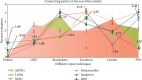
As the scale and depth of artificial intelligence network models continue to increase, their accuracy in albumin recognition tasks has increased rapidly. However, today's small medical datasets are the main reason for the poor recognition of artificial intelligence techniques in this area. The sample size in this article is based on the data analysis and research on urine albumin detection of diabetes in the EI database. It is assumed that the observation group has at least 20 mg UAER difference from the control group, and the standard deviation of the UAER change from baseline to 12 weeks is 30 mg. Therefore, the sample size of the two groups is 77 cases. Assuming that the rate of loss to follow-up during the follow-up period is 20%, at least 92 patients are needed. The final enrollment in this study is 100 patients. Studies have shown that DR is used as an indicator to diagnose NDRD, and its OR value is as high as 28.198, indicating that non-DR can be used as an indicator to distinguish DN from NDRD. The meta-analysis found that DR has a sensitivity of 0.65 and a specificity of 0.75 in distinguishing DN from NDRD in patients with type 2 diabetes, and it is emphasized that PDR is highly specific in the diagnosis of DN. Using a meta-analysis to systematically analyze 45 studies, it was found that the sensitivity of DR to diagnose DN was 0.67, the specificity was 0.78, and the specificity of PDR to predict DN was 0.99, indicating that DR is a good indicator for predicting DN, and the team's latest research has also verified this point of view. They have established a new model for diagnosing DN. In addition to including traditional proteinuria, glycosylated hemoglobin, FR, blood pressure, and other indicators into the diagnostic model, it will also include the presence or absence of DR. The final external verification accuracy rate of this model is 0.875.
Copyright © 2021 Sitong Lin and Yushan Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
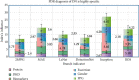
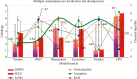

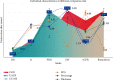
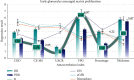
References
-
- Shankar K., Zhang Y., Liu Y., Wu L., Chen C.-H. Hyperparameter tuning deep learning for diabetic retinopathy fundus image classification. IEEE Access. 2020;8 doi: 10.1109/access.2020.3005152. Early Access. - DOI
-
- Knobel D. The presence and consequence of nonalbuminuric chronic kidney disease in patients with type 1 diabetes. Preventive Veterinary Medicine. 2019;38(11):28–33. - PubMed
-
- Mise K., Hoshino J., Ueno T., et al. Clinical and pathological predictors of estimated GFR decline in patients with type 2 diabetes and overt proteinuric diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Metabolism Research and Reviews. 2020;31(6):572–581. - PubMed
-
- An Y., Xu F., Le W., et al. Renal histologic changes and the outcome in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation: Official Publication of the European Dialysis and Transplant Association-European Renal Association. 2020;30(2):257–266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

