Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis Leading to Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
- PMID: 33777582
- PMCID: PMC7989973
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.13497
Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis Leading to Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Abstract
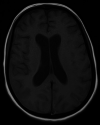
Dural venous sinus thrombosis (DVST) leading to subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is rarely reported in the literature. A 25-year-old primigravida with a history of pre-eclampsia presented with sudden onset headache, confusion, and loss of consciousness. Examination revealed bilateral equivocal planters and bilateral papillary edema. MRI and magnetic resonance venography (MRV) showed the right sinus thrombosis with elements of SAH. The coagulation profile was unremarkable. She was commenced on low molecular weight heparin with periodic monitoring of her Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS). Her condition started improving gradually. Repeat MRI and MRV after 10 days showed resolution of thrombosis and SAH. She was discharged with follow-up, and she was doing well on her recent visit two weeks later.
Keywords: cerebral venous sinus thrombosis; dural venous sinus thrombosis; subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Copyright © 2021, Kumar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage as the initial presentation of dural sinus thrombosis. Oppenheim C, Domigo V, Gauvrit JY, Lamy C, Mackowiak-Cordoliani MA, Pruvo JP, Méder JF. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15760875/ AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005;26:614–617. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage: a rare presentation of cerebral venous thrombosis. Sztajzel R, Coeytaux A, Dehdashti AR, Delavelle J, Sinnreich M. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11703476/ Headache. 2001;41:889–892. - PubMed
-
- Localized convexity subarachnoid haemorrhage—a sign of early cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. Panda S, Prashantha DK, Ravi Shankar S, Nagaraja D. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17:1249–1258. - PubMed
-
- Cortical subarachnoid hemorrhage caused by cerebral venous thrombosis. Oda S, Shimoda M, Hoshikawa K, Osada T, Yoshiyama M, Matsumae M. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 2011;51:30–36. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
