Prediction of Post-hepatectomy Liver Failure in Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on Radiomics Using Gd-EOB-DTPA-Enhanced MRI: The Liver Failure Model
- PMID: 33777748
- PMCID: PMC7987905
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.605296
Prediction of Post-hepatectomy Liver Failure in Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on Radiomics Using Gd-EOB-DTPA-Enhanced MRI: The Liver Failure Model
Abstract
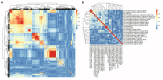
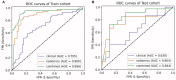
Objectives: Preoperative prediction of post-hepatectomy liver failure (PHLF) in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is significant for developing appropriate treatment strategies. We aimed to establish a radiomics-based clinical model for preoperative prediction of PHLF in HCC patients using gadolinium-ethoxybenzyl-diethylenetriamine (Gd-EOB-DTPA)-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Methods: A total of 144 HCC patients from two medical centers were included, with 111 patients as the training cohort and 33 patients as the test cohort, respectively. Radiomics features and clinical variables were selected to construct a radiomics model and a clinical model, respectively. A combined logistic regression model, the liver failure (LF) model that incorporated the developed radiomics signature and clinical risk factors was then constructed. The performance of these models was evaluated and compared by plotting the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and calculating the area under the curve (AUC) with 95% confidence interval (CI). Results: The radiomics model showed a higher AUC than the clinical model in the training cohort and the test cohort for predicting PHLF in HCC patients. Moreover, the LF model had the highest AUCs in both cohorts [0.956 (95% CI: 0.955-0.962) and 0.844 (95% CI: 0.833-0.886), respectively], compared with the radiomics model and the clinical model. Conclusions: We evaluated quantitative radiomics features from MRI images and presented an externally validated radiomics-based clinical model, the LF model for the prediction of PHLF in HCC patients, which could assist clinicians in making treatment strategies before surgery.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; magnetic resonance imaging; post-hepatectomy liver failure; prediction model; radiomics.
Copyright © 2021 Chen, Liu, Mo, Li, Zhou, Peng, Li and Kuang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Preoperative prediction of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular cancer: a radiomics model using Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI.Eur Radiol. 2019 Sep;29(9):4648-4659. doi: 10.1007/s00330-018-5935-8. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Eur Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30689032
-
Pretreatment prediction of immunoscore in hepatocellular cancer: a radiomics-based clinical model based on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI imaging.Eur Radiol. 2019 Aug;29(8):4177-4187. doi: 10.1007/s00330-018-5986-x. Epub 2019 Jan 21. Eur Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30666445
-
Radiomics model based on preoperative gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI for predicting liver failure.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Mar 21;26(11):1208-1220. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i11.1208. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32231424 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics for preoperative prediction of early recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2023 Jun 7;13:1114983. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1114983. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37350952 Free PMC article.
-
Progress of MRI Radiomics in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Sep 20;11:698373. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.698373. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34616673 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Whole-liver histogram analysis of hepatocyte-specific contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for predicting progression in patients with cirrhosis.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Aug 1;14(8):6072-6086. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-109. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 39144000 Free PMC article.
-
Current status of magnetic resonance imaging radiomics in hepatocellular carcinoma: A quantitative review with Radiomics Quality Score.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Jan 28;30(4):381-417. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i4.381. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38313230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress of MRI-based radiomics in hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2025 Feb 6;15:1420599. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1420599. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39980543 Free PMC article.
-
An update on radiomics techniques in primary liver cancers.Infect Agent Cancer. 2022 Mar 4;17(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13027-022-00422-6. Infect Agent Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35246207 Free PMC article.
-
Liver Resection for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Recent Advances.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2025 Jan-Feb;15(1):102401. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2024.102401. Epub 2024 Aug 10. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 39286759 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

