Volumetric Quantitative Ablation Margins for Assessment of Ablation Completeness in Thermal Ablation of Liver Tumors
- PMID: 33777768
- PMCID: PMC7988092
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.623098
Volumetric Quantitative Ablation Margins for Assessment of Ablation Completeness in Thermal Ablation of Liver Tumors
Abstract
Background: In thermal ablation of liver tumors, complete coverage of the tumor volume by the ablation volume with a sufficient ablation margin is the most important factor for treatment success. Evaluation of ablation completeness is commonly performed by visual inspection in 2D and is prone to inter-reader variability. This work aimed to introduce a standardized approach for evaluation of ablation completeness after CT-guided thermal ablation of liver tumors, using volumetric quantitative ablation margins (QAM).
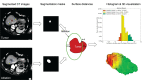
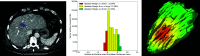
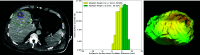
Methods: A QAM computation metric based on volumetric segmentations of tumor and ablation areas and signed Euclidean surface distance maps was developed, including a novel algorithm to address QAM computation in subcapsular tumors. The code for QAM computation was verified in artificial examples of tumor and ablation spheres simulating varying scenarios of ablation margins. The applicability of the QAM metric was investigated in representative cases extracted from a prospective database of colorectal liver metastases (CRLM) treated with stereotactic microwave ablation (SMWA).
Results: Applicability of the proposed QAM metric was confirmed in artificial and clinical example cases. Numerical and visual options of data presentation displaying substrata of QAM distributions were proposed. For subcapsular tumors, the underestimation of tumor coverage by the ablation volume when applying an unadjusted QAM method was confirmed, supporting the benefits of using the proposed algorithm for QAM computation in these cases. The computational code for developed QAM was made publicly available, encouraging the use of a standard and objective metric in reporting ablation completeness and margins.
Conclusion: The proposed volumetric approach for QAM computation including a novel algorithm to address subcapsular liver tumors enables precision and reproducibility in the assessment of ablation margins. The quantitative feedback on ablation completeness opens possibilities for intra-operative decision making and for refined analyses on predictability and consistency of local tumor control after thermal ablation of liver tumors.
Keywords: ablation techniques; computer-assisted therapies; interventional radiology; liver neoplasms; stereotactic techniques.
Copyright © 2021 Sandu, Paolucci, Ruiter, Sznitman, de Jong, Freedman, Weber and Tinguely.
Conflict of interest statement
SW is co-founder and shareholder of CAScination, the manufacturer of one of the navigation systems applied for stereotactic microwave ablation of colorectal liver metastases in the clinical example cases analyzed in this study. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

