Mutational Profile and Clonal Evolution of Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
- PMID: 33777778
- PMCID: PMC7992425
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.628807
Mutational Profile and Clonal Evolution of Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
Abstract
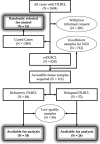
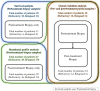
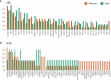
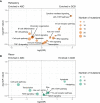
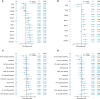
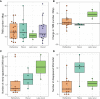
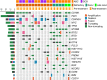
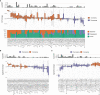
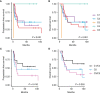
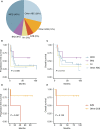
Primary refractory/relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (rrDLBCL) is an unresolved issue for DLBCL treatment and new treatments to overcome resistance is required. To explore the genetic mechanisms underlying treatment resistance in rrDLBCL and to identify candidate genes, we performed targeted deep sequencing of 430 lymphoma-related genes from 58 patients diagnosed with rrDLBCL. Genetic alterations found between the initial biopsy and biopsy at recurrence or refractory disease were investigated. The genes most frequently altered (> 20%) were (in decreasing order of frequency) CDKN2A, PIM1, CD79B, TP53, MYD88, MYC, BTG2, BTG1, CDKN2B, DTX1, CD58, ETV6, and IRF4. Genes mutation of which in pretreatment sample were associated with poor overall survival included NOTCH1, FGFR2, BCL7A, BCL10, SPEN and TP53 (P < 0.05). FGFR2, BCL2, BCL6, BCL10, and TP53 were associated with poor progression-free survival (P < 0.05). Most mutations were truncal and were maintained in both the initial biopsy and post-treatment biopsy with high dynamics of subclones. Immune-evasion genes showed increased overall mutation frequency (CD58, B2M) and variant allele fraction (CD58), and decreased copy number (B2M, CD70) at the post-treatment biopsy. Using the established mutational profiles and integrative analysis of mutational evolution, we identified information about candidate genes that may be useful for the development of future treatment strategies.
Keywords: chemotherapy resistance; immune evasion; next-generation sequencing (NGS); prognostic marker; refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; tumor evolution.
Copyright © 2021 Lee, Lee, Cho, Yoon, Kim, Park, Kim and Ko.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Specific Mutation Predict Relapse/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma.J Blood Med. 2024 Sep 10;15:407-419. doi: 10.2147/JBM.S471639. eCollection 2024. J Blood Med. 2024. PMID: 39279878 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations or copy number losses of CD58 and TP53 genes in diffuse large B cell lymphoma are independent unfavorable prognostic factors.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 13;7(50):83294-83307. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13065. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27825110 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Landscapes of Relapsed and Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphomas.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 May 1;22(9):2290-300. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2123. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26647218
-
Hitting back at lymphoma: How do modern diagnostics identify high-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma subsets and alter treatment?Cancer. 2019 Sep 15;125(18):3111-3120. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32145. Epub 2019 Jul 9. Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31287161 Review.
-
The pathobiology of primary testicular diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Implications for novel therapies.Blood Rev. 2018 May;32(3):249-255. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2017.12.001. Epub 2017 Dec 20. Blood Rev. 2018. PMID: 29289361 Review.
Cited by
-
Specific Mutation Predict Relapse/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma.J Blood Med. 2024 Sep 10;15:407-419. doi: 10.2147/JBM.S471639. eCollection 2024. J Blood Med. 2024. PMID: 39279878 Free PMC article.
-
Relapse Timing Is Associated With Distinct Evolutionary Dynamics in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma.J Clin Oncol. 2023 Sep 1;41(25):4164-4177. doi: 10.1200/JCO.23.00570. Epub 2023 Jun 15. J Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37319384 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating tumor DNA - from biology to potential clinical applications in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas.Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2025;29(2):150-158. doi: 10.5114/wo.2025.150452. Epub 2025 May 9. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2025. PMID: 40620893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating tumor DNA in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: analysis of response assessment, correlation with PET/CT and clone evolution.Hematol Transfus Cell Ther. 2024 Dec;46 Suppl 6(Suppl 6):S241-S249. doi: 10.1016/j.htct.2024.07.005. Epub 2024 Sep 20. Hematol Transfus Cell Ther. 2024. PMID: 39317576 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics and predictive model for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with early chemoimmunotherapy failure.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 16;16:1553850. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1553850. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40589747 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coiffier B, Thieblemont C, Van Den Neste E, Lepeu G, Plantier I, Castaigne S, et al. . Long-term outcome of patients in the LNH-98.5 trial, the first randomized study comparing rituximab-CHOP to standard CHOP chemotherapy in DLBCL patients: a study by the Groupe d’Etudes des Lymphomes de l’Adulte. Blood (2010) 116:2040–5. 10.1182/blood-2010-03-276246 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

