Identification of a Risk Stratification Model to Predict Overall Survival and Surgical Benefit in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma With Distant Metastasis
- PMID: 33777784
- PMCID: PMC7991397
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.630842
Identification of a Risk Stratification Model to Predict Overall Survival and Surgical Benefit in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma With Distant Metastasis
Abstract
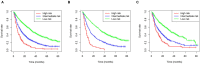
Background: Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is the main subtype of renal cell carcinoma and has different prognoses, especially in patients with metastasis. Here, we aimed to establish a novel model to predict overall survival (OS) and surgical benefit of ccRCC patients with distant metastasis. Methods: Using data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) databases, we identified 2185 ccRCC patients with distant metastasis diagnosed from 2010 to 2015. Univariate and multivariate Cox analysis were used to identify significant prognostic clinicopathological variables. By integrating these variables, a prognostic nomogram was constructed and evaluated using C-indexes and calibration curves. The discriminative ability of the nomogram was measured by analyses of receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. A risk stratification model was built according to each patient's total scores. Kaplan-Meier curves were performed in the low-, intermediate- and high-risk groups to evaluate the survival benefit of surgery. Results: Eight clinicopathological variables were included as independent prognostic factors in the nomogram: grade, marital status, T stage, N stage, bone metastasis, brain metastasis, liver metastasis, and lung metastasis. The nomogram had a better discriminative ability for predicting OS than Tumor-Node-Metastasis (TNM) stage. The C-index was 0.71 (95% CI 0.68-0.74) in the training cohort. The calibration plots demonstrated that the nomogram-based predictive outcomes had good consistency with the actual prognosis results. Total nephrectomy improved prognosis in both the low-risk and intermediate-risk groups, but partial nephrectomy could only benefit the low-risk group. Conclusions: We constructed a predictive nomogram and risk stratification model to evaluate prognosis in ccRCC patients with distant metastasis, which was valuable for prognostic stratification and making therapeutic decisions.
Keywords: clear cell renal cell carcinoma; distant metastasis; nomogram; overall survival; surgical benefit.
Copyright © 2021 Chen, Cao, Li and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Ko JJ, Xie W, Kroeger N, Lee JL, Rini BI, Knox JJ, et al. The international metastatic renal cell carcinoma database consortium model as a prognostic tool in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma previously treated with first-line targeted therapy: a population-based study. Lancet Oncol. (2015) 16:293–300. 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)71222-7 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

