Procalcitonin and C-Reactive Protein/Procalcitonin Ratio as Markers of Infection in Patients With Solid Tumors
- PMID: 33777975
- PMCID: PMC7994271
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.627967
Procalcitonin and C-Reactive Protein/Procalcitonin Ratio as Markers of Infection in Patients With Solid Tumors
Abstract
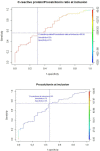
Objectives: The roles of procalcitonin (PCT) and C-reactive protein (CRP) in febrile cancer patients is currently unclear. Our aim was to assess these in febrile patients with solid tumors and to identify cut-off values for ruling out infection. Methods: We retrospectively evaluated patients with solid tumors admitted to hospital due to fever. They were divided into those with Fever with microbiologically documented infection (FMDI), Fever with clinically documented infection (FCDI) and Tumor-related fever (TRF). PCT and CRP levels were compared. Receiver-operating curves were plotted to define the best cut-off values for discriminating between infection-related and cancer-related fever. Results: Between January 2015 to November 2018, 131 patients were recorded (mean age 68 years, 67% male, 86% with metastasis). Patients with FMDI or FCDI had significantly higher baseline levels of PCT and lower CRP/PCT than those with TRF. A PCT cut-off value of 0.52 ng/mL for discriminating between infection and cancer-associated fever yielded 75% sensitivity, 55% specificity, 77% positive predictive value (PPV), and 52% negative predictive value (NPV). A CRP/PCT ratio with a cut-off value of 95 showed 56% sensitivity, 70% specificity, 79% NPV, and 44% PPV. Discussion: PCT is a sensitive marker of sepsis or localized infection in patients with solid tumors, but its specificity is poor. The CRP/PCT ratio improves specificity, thus providing a reliable means of ruling out infection for values above 95.
Keywords: C-reactive protein/procalcitonin ratio; fever; infection; procalcitonin; solid tumor.
Copyright © 2021 Vassallo, Michelangeli, Fabre, Manni, Genillier, Weiss, Blanchouin, Saudes, Kaphan, Puchois, Pradier and Montagne.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dusemund F, Bucher B, Meyer S, Thomann R, Kühn F, Bassetti S, et al. . Influence of procalcitonin on decision to start antibiotic treatment in patients with a lower respiratory tract infection: insight from the observational multicentric ProREAL surveillance. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. (2013) 32:51–60. 10.1007/s10096-012-1713-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Townsend J, Adams V, Galiatsatos P, Pearse D, Pantle H, Masterson M, et al. . Procalcitonin-guided antibiotic therapy reduces antibiotic use for lower respiratory tract infections in a United States medical center: results of a clinical trial. Open Forum Infect Dis. (2018) 5:ofy327. 10.1093/ofid/ofy327 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous