Feprazone Ameliorates TNF-α-Induced Loss of Aggrecan via Inhibition of the SOX-4/ADAMTS-5 Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 33778274
- PMCID: PMC7992146
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.0c06212
Feprazone Ameliorates TNF-α-Induced Loss of Aggrecan via Inhibition of the SOX-4/ADAMTS-5 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
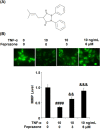
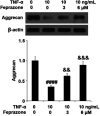
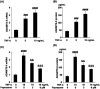
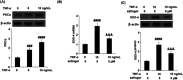
Background: Arthritis is a cartilage degenerative disease that is mainly induced by the degradation of the cartilage extracellular matrix (ECM), which is found to be regulated by the expression level of a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 5 (ADAMT-5), an enzyme degrading Aggrecans in the ECM. Feprazone is a classic nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug with promising efficacy in arthritis. The present study aims to investigate the protective effect of Feprazone on the degraded Aggrecan in the human chondrocytes induced with tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and to clarify the underlying mechanism. Methods: To investigate the effect of Feprazone, the CHON-001 chondrocytes were stimulated with TNF-α (10 ng/mL) in the presence or absence of Feprazone (3, 6 μM) for 24 h. Mitochondrial membrane potential was evaluated using the Rhodamine 123 assay. The gene expressions of interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-8 (IL-8), monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1), and ADAMTS-5 in the treated chondrocytes were detected using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), and the protein levels of these targets were determined using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). SOX-4 was knocked down by transfecting the siRNA into the chondrocytes. Western blot analysis was utilized to evaluate the expression levels of SOX-4, Aggrecan, and protein kinase C (PKCα). Results: First, the reduced mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) and secretion of proinflammatory factors (IL-1β, IL-8, and MCP-1) induced by TNF-α were significantly reversed by treatment with Feprazone. Second, the expression of Aggrecan was significantly decreased by stimulation with TNF-α via upregulation of ADAMTS-5 but was dramatically reversed by the introduction of Feprazone. Third, we found that TNF-α elevated the expression of ADAMTS-5 by upregulating SOX-4, which was observed to be related to the activation of PKCα. Lastly, the elevated expression of SOX-4 induced by TNF-α was significantly reversed by Feprazone. Conclusions: Feprazone might ameliorate TNF-α-induced loss of Aggrecan via the inhibition of the SOX-4/ADAMTS-5 signaling pathway.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
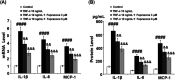
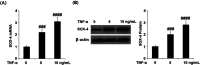
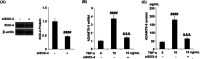
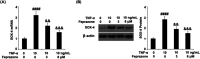
Similar articles
-
Azilsartan prevented AGE-induced inflammatory response and degradation of aggrecan in human chondrocytes through inhibition of Sox4.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2021 Aug;35(8):e22827. doi: 10.1002/jbt.22827. Epub 2021 May 29. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 34051020
-
Feprazone Mitigates IL-1β-Induced Cellular Senescence in Chondrocytes.ACS Omega. 2021 Mar 31;6(14):9442-9448. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c06066. eCollection 2021 Apr 13. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 33869924 Free PMC article.
-
IL-21 Enhances the Degradation of Cartilage Through the JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway During Osteonecrosis of Femoral Head Cartilage.Inflammation. 2018 Mar;41(2):595-605. doi: 10.1007/s10753-017-0715-1. Inflammation. 2018. PMID: 29247327
-
[Parthenolide inhibits tumor necrosis factor-alpha induced catabolism of aggrecan in chondrocytes in osteoarthritis: in vitro experiment with cultured human chondrocytes].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008 Mar 18;88(11):764-8. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 18683686 Chinese.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein-7 antagonizes tumor necrosis factor-α-induced activation of nuclear factor κB and up-regulation of the ADAMTS, leading to decreased degradation of disc matrix macromolecules aggrecan and collagen II.Spine J. 2014 Mar 1;14(3):505-12. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2013.08.016. Epub 2013 Oct 29. Spine J. 2014. PMID: 24176808
Cited by
-
The therapeutic effects of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound in musculoskeletal soft tissue injuries: Focusing on the molecular mechanism.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Dec 16;10:1080430. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1080430. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36588943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating anticancer activity of emodin by enhancing antioxidant activities and affecting PKC/ADAMTS4 pathway in thioacetamide-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rats.Redox Rep. 2024 Dec;29(1):2365590. doi: 10.1080/13510002.2024.2365590. Epub 2024 Jun 11. Redox Rep. 2024. PMID: 38861483 Free PMC article.
-
SOXC Transcription Factors as Diagnostic Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets for Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 20;24(4):4215. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044215. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficient Generation of Chondrocytes From Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in a 3D Culture System: Protocol for a Practical Model for Assessing Anti-Inflammatory Therapies.JMIR Res Protoc. 2023 Jul 28;12:e42964. doi: 10.2196/42964. JMIR Res Protoc. 2023. PMID: 37505889 Free PMC article.
-
TNFα-Related Chondrocyte Inflammation Models: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 8;25(19):10805. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910805. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39409134 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haleagrahara N.; Hodgson K.; Miranda-Hernandez S.; Hughes S.; Kulur A. B.; Ketheesan N. Flavonoid quercetin-methotrexate combination inhibits inflammatory mediators and matrix metalloproteinase expression, providing protection to joints in collagen-induced arthritis. Inflammopharmacology 2018, 26, 1219–1232. 10.1007/s10787-018-0464-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lemos G. A.; Rissi R.; de Souza Pires I. L.; de Oliveira L. P.; de Aro A. A.; Pimentel E. R.; Palomari E. T. Low-level laser therapy stimulates tissue repair and reduces the extracellular matrix degradation in rats with induced arthritis in the temporomandibular joint. Lasers. Med. Sci. 2016, 31, 1051–1059. 10.1007/s10103-016-1946-3. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

