Ethyl Pyruvate as a Potential Defense Intervention against Cytokine Storm in COVID-19?
- PMID: 33778286
- PMCID: PMC7992141
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.1c00157
Ethyl Pyruvate as a Potential Defense Intervention against Cytokine Storm in COVID-19?
Abstract
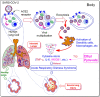
COVID-19 is a deadly pandemic and has resulted in a huge loss of money and life in the past few months. It is well known that the SARS-CoV-2 gene mutates relatively slowly as compared to other viruses but still may create hurdles in developing vaccines. Therefore, there is a need to develop alternative routes for its management and treatment of COVID-19. Based on the severity of viral infection in COVID-19 patients, critically ill patients (∼5%, with old age, and comorbidities) are at high risk of morbidities. The reason for this severity in such patients is attributed to "misleading cytokine storm", which produces ARDS and results in the deaths of critically ill patients. In this connection, ethyl pyruvate (EP) controls these cytokines/chemokines, is an anti-inflammatory agent, and possesses a protective effect on the lungs, brain, heart, and mitochondria against various injuries. Considering these facts, we propose that the site-selective EP formulations (especially aerosols) could be the ultimate adjuvant therapy for the regulation of misleading cytokine storm in severely affected COVID-19 patients and could reduce the mortalities.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 (accessed 30 August 2020).
-
- WHO WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed 01 February 2021).
-
- Callaway E.The coronavirus is mutating — does it matter? https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-020-02544-6 (accessed 02 February 2021). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous