Short-term effects of ambient air pollution and outdoor temperature on biomarkers of myocardial damage, inflammation and oxidative stress in healthy adults
- PMID: 33778346
- PMCID: PMC7939428
- DOI: 10.1097/EE9.0000000000000078
Short-term effects of ambient air pollution and outdoor temperature on biomarkers of myocardial damage, inflammation and oxidative stress in healthy adults
Abstract
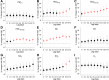
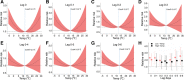
The mechanisms whereby ambient air pollution and temperature changes promote cardiac events remain incompletely described. Seventy-three nonsmoking healthy adults (mean age 23.3, SD 5.4 years) were followed with up to four repeated visits across 15 months in Beijing in 2014-2016. Biomarkers relevant to myocardial damage (high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I [hs-cTnI]), inflammation (growth differentiation factor-15 [GDF-15]), and oxidative stress (8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine [8-OHdG]) were measured at each visit, while ambient air pollution and temperature were monitored throughout the study. Linear mixed-effects models coupled with distributed lag nonlinear models were used to assess the impacts of each exposure measure on study outcomes. During follow-up, average daily concentrations of fine particulate matter and outdoor temperature were 62.9 µg/m3 (8.1-331.0 µg/m3) and 10.1 °C (-6.5°C to 29.5°C). Serum hs-cTnI levels were detectable in 18.2% of blood samples, with 27.4% of individuals having ≥1 detectable values. Higher levels of ambient particulates and gaseous pollutants (per interquartile range) up to 14 days before clinical visits were associated with significant alterations in hs-cTnI levels of 22.9% (95% CI, 6.4, 39.4) to 154.7% (95% CI, 94.4, 215.1). These changes were accompanied by elevations of circulating GDF-15 and urinary 8-OHdG levels. Both low (5th percentile, -2.5 °C) and high (95th percentile, 24.8°C) outdoor temperatures, with breakpoint at ~13.0°C as the reference level, were also associated with elevations of hs-cTnI levels. Short-term exposure to ambient air pollution and temperature was associated with cardiac troponin, a biomarker of myocardial damage, along with increased inflammation and oxidative stress responses. These findings extend our understanding of the biological mechanisms linking pervasive environmental exposure to adverse cardiac events.
Keywords: Air pollution; Cardiac troponin; Myocardial damage; Temperature.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of Environmental Epidemiology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The author/authors declares/declare that they have no conflicts of interest with regard to the content of this report. The results reported herein correspond to specific aims of grant 81773381 to investigator Wei Huang from National Natural Science Foundation of China. This work was (also) supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (81470025) and Peking University Health Science Center-University of Michigan Health System Joint Institute for Clinical and Translational Research, and Peking University Infrastructure Fund for Interdisciplinary Studies (2013-3-02).
Figures



References
-
- Claeys MJ, Rajagopalan S, Nawrot TS, Brook RD. Climate and environmental triggers of acute myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J 201738955–960 - PubMed
-
- Rajagopalan S, Al-Kindi SG, Brook RD. Air pollution and cardiovascular disease: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol 2018722054–2070 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
