Comparison of Original and 2018 Lake Louise Criteria for Diagnosis of Acute Myocarditis: Results of a Validation Cohort
- PMID: 33778510
- PMCID: PMC7978026
- DOI: 10.1148/ryct.2019190010
Comparison of Original and 2018 Lake Louise Criteria for Diagnosis of Acute Myocarditis: Results of a Validation Cohort
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the diagnostic performance of the original Lake Louise criteria (LLC) and the 2018 LLC for the diagnosis of acute myocarditis and simultaneously validate previously reported cutoff values for parametric mapping techniques.
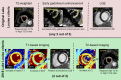
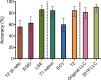
Materials and methods: A total of 40 patients with acute myocarditis and 26 control participants underwent cardiac MRI. Cardiac MRI protocol allowed for assessment of T2 signal intensity ratio, early gadolinium enhancement ratio, late gadolinium enhancement, T1 relaxation times, extracellular volume fraction, and T2 relaxation times. The original and the 2018 LLC were assessed, and differences between sensitivities and specificities were calculated with the McNemar test.
Results: The 2018 LLC yielded a sensitivity of 87.5% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 73.9%, 94.5%) and a specificity of 96.2% (95% CI: 81.1%, 99.3%). The original LLC had a sensitivity of 72.5% (95% CI: 57.2%, 83.9%) and a specificity of 96.2% (95% CI: 81.1%, 99.3%). Sensitivity of the 2018 LLC was significantly higher compared with the sensitivity of original LLC (P = .031). No differences in specificity were observed between both scores (P = .999).
Conclusion: Multiparametric cardiac MRI has a high diagnostic value for the diagnosis of patients clinically suspected of having acute myocarditis. The 2018 LLC further improve the diagnostic performance of cardiac MRI by increasing its sensitivity. An implementation of the new score into routine diagnostic protocols should be considered.© RSNA, 2019See also the commentary by Gutberlet and Lücke in this issue.Supplemental material is available for this article.
2019 by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures of Conflicts of Interest: J.A.L. disclosed no relevant relationships. A.F. disclosed no relevant relationships. A.I. disclosed no relevant relationships. D.D. disclosed no relevant relationships. D.K. disclosed no relevant relationships. A.F. disclosed no relevant relationships. F.C.S. disclosed no relevant relationships. A.M.S. disclosed no relevant relationships. D.T. disclosed no relevant relationships.
Figures

Comment in
-
Original versus 2018 Lake Louise Criteria for Acute Myocarditis Diagnosis: Old versus New.Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging. 2019 Aug 29;1(3):e190150. doi: 10.1148/ryct.2019190150. eCollection 2019 Aug. Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging. 2019. PMID: 33779645 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Caforio AL, Pankuweit S, Arbustini E, et al. . Current state of knowledge on aetiology, diagnosis, management, and therapy of myocarditis: a position statement of the European Society of Cardiology Working Group on Myocardial and Pericardial Diseases. Eur Heart J 2013;34(33):2636–2648, 2648a–2648d. - PubMed
-
- Drory Y, Turetz Y, Hiss Y, et al. . Sudden unexpected death in persons less than 40 years of age. Am J Cardiol 1991;68(13):1388–1392. - PubMed
-
- Pollack A, Kontorovich AR, Fuster V, Dec GW. Viral myocarditis—diagnosis, treatment options, and current controversies. Nat Rev Cardiol 2015;12(11):670–680. - PubMed
-
- Luetkens JA, Schlesinger-Irsch U, Kuetting DL, et al. . Feature-tracking myocardial strain analysis in acute myocarditis: diagnostic value and association with myocardial oedema. Eur Radiol 2017;27(11):4661–4671. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

