Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction: Review of CT and Pathologic Findings
- PMID: 33778654
- PMCID: PMC7978021
- DOI: 10.1148/ryct.2021200314
Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction: Review of CT and Pathologic Findings
Abstract
Chronic lung allograft dysfunction (CLAD) is the most common cause of mortality in lung transplant recipients after the 1st year of transplantation. CLAD has traditionally been classified into two distinct obstructive and restrictive forms: bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome and restrictive allograft syndrome. However, CLAD may manifest with a spectrum of imaging and pathologic findings and a combination of obstructive and restrictive physiologic abnormalities. Although the initial CT manifestations of CLAD may be nonspecific, the progression of findings at follow-up should signal the possibility of CLAD and may be present on imaging studies prior to the development of functional abnormalities of the lung allograft. This review encompasses the evolution of CT findings in CLAD, with emphasis on the underlying pathogenesis and pathologic condition, to enhance understanding of imaging findings. The purpose of this article is to familiarize the radiologist with the initial and follow-up CT findings of the obstructive, restrictive, and mixed forms of CLAD, for which early diagnosis and treatment may result in improved survival. Supplemental material is available for this article. © RSNA, 2021.
2021 by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures of Conflicts of Interest: D.B. disclosed no relevant relationships. R.G.N. disclosed no relevant relationships. J.C.E. disclosed no relevant relationships. J.Y. disclosed no relevant relationships. R.L. disclosed no relevant relationships. C.B. disclosed no relevant relationships. J.R.S. disclosed no relevant relationships. O.M.M. disclosed no relevant relationships. N.L.M. disclosed no relevant relationships. A.M.B. disclosed no relevant relationships.
Figures
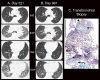
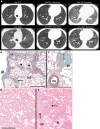

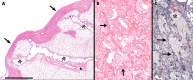
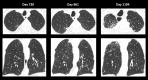
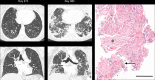
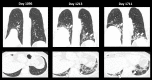
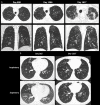
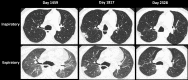

References
-
- Chambers DC, Cherikh WS, Harhay MO, et al. The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: thirty-sixth adult lung and heart-lung transplantation report-2019; focus theme: donor and recipient size match. J Heart Lung Transplant 2019;38(10):1042–1055. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chambers DC, Yusen RD, Cherikh WS, et al. The Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: thirty-fourth adult lung and heart-lung transplantation report-2017; focus theme: allograft ischemic time. J Heart Lung Transplant 2017;36(10):1047–1059. - PubMed
-
- Verleden GM, Glanville AR, Lease ED, et al. Chronic lung allograft dysfunction: definition, diagnostic criteria, and approaches to treatment: a consensus report from the Pulmonary Council of the ISHLT. J Heart Lung Transplant 2019;38(5):493–503. - PubMed
-
- Sumpter TL, Wilkes DS. Role of autoimmunity in organ allograft rejection: a focus on immunity to type V collagen in the pathogenesis of lung transplant rejection. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2004;286(6):L1129–L1139. - PubMed
-
- Glanville AR. Bronchoscopic monitoring after lung transplantation. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 2010;31(2):208–221. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

