MRI Assessment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Local-Regional Therapy: A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 33778692
- PMCID: PMC7983779
- DOI: 10.1148/rycan.2020190024
MRI Assessment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Local-Regional Therapy: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
Nearly 80% of cirrhotic patients diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are not eligible for surgical resection and instead undergo local-regional treatment. After therapy for HCC, patients undergo imaging surveillance to assess treatment efficacy and identify potential sites of progressive tumor elsewhere within the liver. Accurate interpretation of posttreatment imaging is essential for guiding further management decisions, and radiologists must understand expected treatment-specific imaging findings for each of the local-regional therapies. Of interest, expected imaging findings seen after radiation-based therapies (transarterial radioembolization and stereotactic body radiation therapy) are different than those seen after thermal ablation and transarterial chemoembolization. Given differences in expected posttreatment imaging findings, the current radiologic treatment response assessment algorithms used for HCC (modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors classification, European Association for the Study of Liver Diseases criteria, and Liver Imaging and Reporting Data System Treatment Response Algorithm) must be applied cautiously for radiation-based therapies in which persistent arterial phase hyperenhancement in the early posttreatment period is common and expected. This article will review the concept of tumor response assessment for HCC, the forms of local-regional therapy for HCC, and the expected posttreatment findings for each form of therapy. Keywords: Abdomen/GI, Liver, MR-Imaging, Treatment Effects, Tumor Response © RSNA, 2020.
2020 by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures of Conflicts of Interest: M.M. disclosed no relevant relationships. W.R.M. disclosed no relevant relationships. K.S. disclosed no relevant relationships. A.Z. disclosed no relevant relationships. A.S.J. disclosed no relevant relationships. S.M. disclosed no relevant relationships. A.A. disclosed no relevant relationships. K.E.M. Activities related to the present article: disclosed no relevant relationships. Activities not related to the present article: receives royalties from Wolters Kluwer and Elsevier. Other relationships: disclosed no relevant relationships. M.S.D. Activities related to the present article: disclosed no relevant relationships. Activities not related to the present article: receives royalties from Wolters Kluwer and uptodate.com. Other relationships: disclosed no relevant relationships.
Figures
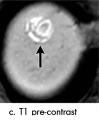


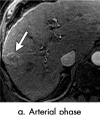

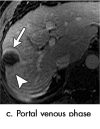





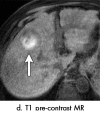


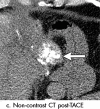
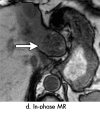
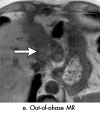
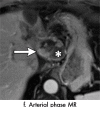
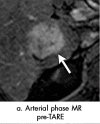

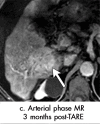
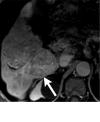
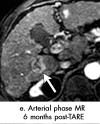
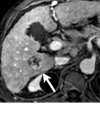



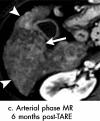
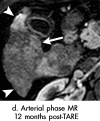

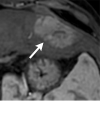



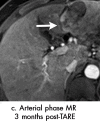


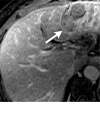

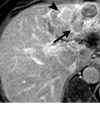


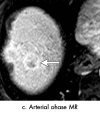
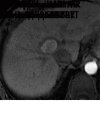

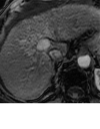
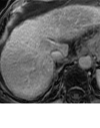
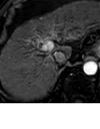





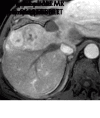
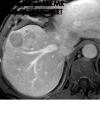
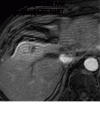
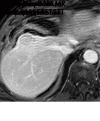
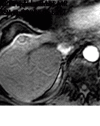

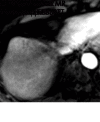

References
-
- Marrero JA, Kulik LM, Sirlin CB, et al. Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2018 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018;68(2):723–750. - PubMed
-
- Gamblin TC, Geller DA. Downstaging hepatocellular carcinoma prior to liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 2005;11(12):1466–1468. - PubMed
-
- Mora RA, Ali R, Gabr A, et al. Pictorial essay: imaging findings following Y90 radiation segmentectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Abdom Radiol (NY) 2018;43(7):1723–1738. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

