IMAGE QUALITY AND POTENTIAL DOSE REDUCTION USING ADVANCED MODELED ITERATIVE RECONSTRUCTION (ADMIRE) IN ABDOMINAL CT - A REVIEW
- PMID: 33778892
- PMCID: PMC8507455
- DOI: 10.1093/rpd/ncab020
IMAGE QUALITY AND POTENTIAL DOSE REDUCTION USING ADVANCED MODELED ITERATIVE RECONSTRUCTION (ADMIRE) IN ABDOMINAL CT - A REVIEW
Abstract
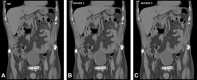
Traditional filtered back projection (FBP) reconstruction methods have served the computed tomography (CT) community well for over 40 years. With the increased use of CT during the last decades, efforts to minimise patient exposure, while maintaining sufficient or improved image quality, have led to the development of model-based iterative reconstruction (MBIR) algorithms from several vendors. The usefulness of the advanced modeled iterative reconstruction (ADMIRE) (Siemens Healthineers) MBIR in abdominal CT is reviewed and its noise suppression and/or dose reduction possibilities explored. Quantitative and qualitative methods with phantom and human subjects were used. Assessment of the quality of phantom images will not always correlate positively with those of patient images, particularly at the higher strength of the ADMIRE algorithm. With few exceptions, ADMIRE Strength 3 typically allows for substantial noise reduction compared to FBP and hence to significant (≈30%) patient dose reductions. The size of the dose reductions depends on the diagnostic task.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of ADMIRE, SAFIRE, and Filtered Back Projection in Standard and Low-Dose Non-Enhanced Head CT.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jun 17;15(12):1541. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15121541. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40564860 Free PMC article.
-
Development, validation, and application of a generic image-based noise addition method for simulating reduced dose computed tomography images.Med Phys. 2025 Jan;52(1):171-187. doi: 10.1002/mp.17444. Epub 2024 Oct 10. Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 39387993 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of image quality in abdominal CT: potential dose reduction with model-based iterative reconstruction.Eur Radiol. 2018 Jun;28(6):2464-2473. doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-5113-4. Epub 2018 Jan 24. Eur Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29368163 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation dose and diagnostic image quality associated with iterative reconstruction in coronary CT angiography: A systematic review.J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2016 Aug;60(4):459-68. doi: 10.1111/1754-9485.12473. Epub 2016 May 30. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27241506
-
The effect of deep learning reconstruction on abdominal CT densitometry and image quality: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Radiol. 2022 May;32(5):2921-2929. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-08438-z. Epub 2021 Dec 15. Eur Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34913104 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Learning effects in visual grading assessment of model-based reconstruction algorithms in abdominal Computed Tomography.Eur J Radiol Open. 2023 May 6;10:100490. doi: 10.1016/j.ejro.2023.100490. eCollection 2023. Eur J Radiol Open. 2023. PMID: 37207049 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of Iterative Reconstruction in Image Space Algorithm in Combination with Automatic Tube Current Modulation Compared to Filtered Back Projection in Brain CT Scan.J Biomed Phys Eng. 2024 Aug 1;14(4):379-388. doi: 10.31661/jbpe.v0i0.2404-1741. eCollection 2024 Aug. J Biomed Phys Eng. 2024. PMID: 39175556 Free PMC article.
-
[Deep Learning Reconstruction Algorithm Combined With Smart Metal Artifact Reduction Technique Improves Image Quality of Upper Abdominal CT in Critically Ill Patients].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Nov 20;55(6):1403-1409. doi: 10.12182/20241160102. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 39990832 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
GaN Heterostructures as Innovative X-ray Imaging Sensors-Change of Paradigm.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Jan 19;13(2):147. doi: 10.3390/mi13020147. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35208272 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kataria, B. Visual Grading Evaluation of Reconstruction Methods and Dose Optimisation in Abdominal Computed Tomography. Doctoral Thesis. (Linköping, Sweden: Linköping University; ) (2019).
-
- Qiu, D. and Seeram, E. Does iterative reconstruction improve image quality and reduce dose in computed tomography? Radiol Open J. 1(2), 42–54 (2016).
-
- Aurumsköljd, M.-L. Optimisation of image quality and radiation dose in computed tomography using iterative image reconstruction. Doctoral Thesis. (Lund, Sweden: Lund University; ) (2017).
-
- Ippolito, D., Maino, C., Riva, L., Pecorelli, A., Vito, A., Lombardi, S., Ragusi, M., Giandola, T., Talei Franzesi, T. and Sironi, S. Iterative model-based CT reconstruction algorithm the background and added clinical value review paper. J Radiological Review 7(3), 185–195 (2020).
-
- Ehman, E. C. et al. Methods for clinical evaluation of noise reduction techniques in abdominopelvic CT. Radio Graphics 34, 849–862 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

