IMAGE QUALITY AND POTENTIAL DOSE REDUCTION USING ADVANCED MODELED ITERATIVE RECONSTRUCTION (ADMIRE) IN ABDOMINAL CT - A REVIEW
- PMID: 33778892
- PMCID: PMC8507455
- DOI: 10.1093/rpd/ncab020
IMAGE QUALITY AND POTENTIAL DOSE REDUCTION USING ADVANCED MODELED ITERATIVE RECONSTRUCTION (ADMIRE) IN ABDOMINAL CT - A REVIEW
Abstract
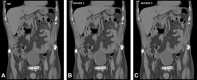
Traditional filtered back projection (FBP) reconstruction methods have served the computed tomography (CT) community well for over 40 years. With the increased use of CT during the last decades, efforts to minimise patient exposure, while maintaining sufficient or improved image quality, have led to the development of model-based iterative reconstruction (MBIR) algorithms from several vendors. The usefulness of the advanced modeled iterative reconstruction (ADMIRE) (Siemens Healthineers) MBIR in abdominal CT is reviewed and its noise suppression and/or dose reduction possibilities explored. Quantitative and qualitative methods with phantom and human subjects were used. Assessment of the quality of phantom images will not always correlate positively with those of patient images, particularly at the higher strength of the ADMIRE algorithm. With few exceptions, ADMIRE Strength 3 typically allows for substantial noise reduction compared to FBP and hence to significant (≈30%) patient dose reductions. The size of the dose reductions depends on the diagnostic task.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
References
-
- Kataria, B. Visual Grading Evaluation of Reconstruction Methods and Dose Optimisation in Abdominal Computed Tomography. Doctoral Thesis. (Linköping, Sweden: Linköping University; ) (2019).
-
- Qiu, D. and Seeram, E. Does iterative reconstruction improve image quality and reduce dose in computed tomography? Radiol Open J. 1(2), 42–54 (2016).
-
- Aurumsköljd, M.-L. Optimisation of image quality and radiation dose in computed tomography using iterative image reconstruction. Doctoral Thesis. (Lund, Sweden: Lund University; ) (2017).
-
- Ippolito, D., Maino, C., Riva, L., Pecorelli, A., Vito, A., Lombardi, S., Ragusi, M., Giandola, T., Talei Franzesi, T. and Sironi, S. Iterative model-based CT reconstruction algorithm the background and added clinical value review paper. J Radiological Review 7(3), 185–195 (2020).
-
- Ehman, E. C. et al. Methods for clinical evaluation of noise reduction techniques in abdominopelvic CT. Radio Graphics 34, 849–862 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

