Comparison of the Prognostic Outcome between High-Grade Ovarian Sertoli-Leydig Cell Tumors (SLCTs) and Low-Grade SLCTs
- PMID: 33779091
- PMCID: PMC8007424
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2021.62.4.366
Comparison of the Prognostic Outcome between High-Grade Ovarian Sertoli-Leydig Cell Tumors (SLCTs) and Low-Grade SLCTs
Abstract
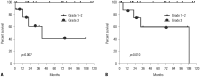
The purpose of the current study was to compare prognostic outcomes between patients with high-grade ovarian Sertoli-Leydig cell tumors (SLCTs) and those with other low-grade SLCTs. We retrospectively reviewed medical records for 24 patients pathologically diagnosed with SLCTs between 2006 to 2019 at two institutions. The patients were grouped according to pathological grade: SLCT was classified as grade 1, well differentiated; grade 2, intermediated differentiated; or grade 3, poorly differentiated (Meyer's classification). Statistical analysis was performed to compare survival outcomes according to pathological grade. The median patient age was 42.5 years (range 16-75). Eighteen patients (75%) were International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics stage I, and none were diagnosed in stage IV. Nine patients (37.5%) were grade 3, and 15 patients (63.5%) were grades 1-2. When comparing clinical baseline characteristics of the grade 1-2 group with those of the grade 3 group, only serum CA125 level at diagnosis was significantly higher in the grade 3 group (38.34 vs. 382.29, p=0.002). Five patients experienced recurrence of grade 3 disease, while no recurrence was reported in grade 1-2 disease. Four of the five recurrent patients died. In result, grade 3 ovarian SLCT showed significantly poorer prognosis than grade 1-2 disease (overall survival, hazard ratio=14.25, 95% confidence interval=1.881-108.0; log-rank p=0.010). Our findings were consistent with the concept that patients with stage I/grade 1-2 tumors have a good prognosis without adjuvant chemotherapy. Since grade 3 ovarian SLCT appears to be relatively more fatal than grade 1 or 2, patients with grade 3 SLCT might require more aggressive surgical intervention and post-treatment surveillance.
Keywords: Ovarian Sertoli-Leydig cell tumors; chemotherapy; prognosis.
© Copyright: Yonsei University College of Medicine 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Zaloudek C, Norris HJ. Sertoli-Leydig tumors of the ovary. A clinicopathologic study of 64 intermediate and poorly differentiated neoplasms. Am J Surg Pathol. 1984;8:405–418. - PubMed
-
- Sachdeva P, Arora R, Dubey C, Sukhija A, Daga M, Singh DK. Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor: a rare ovarian neoplasm. Case report and review of literature. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2008;24:230–234. - PubMed
-
- Bhat RA, Lim YK, Chia YN, Yam KL. Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor of the ovary: analysis of a single institution database. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2013;39:305–310. - PubMed
-
- Gee DC, Russell P. The pathological assessment of ovarian neoplasms. IV: The sex cord-stromal tumours. Pathology. 1981;13:235–255. - PubMed
-
- Roth LM, Anderson MC, Govan AD, Langley FA, Gowing NF, Woodcock AS. Sertoli-Leydig cell tumors: a clinicopathologic study of 34 cases. Cancer. 1981;48:187–197. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

