Patient-Reported Outcomes in Patients With PIK3CA-Mutated Hormone Receptor-Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative Advanced Breast Cancer From SOLAR-1
- PMID: 33780274
- PMCID: PMC8210974
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.20.01139
Patient-Reported Outcomes in Patients With PIK3CA-Mutated Hormone Receptor-Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative Advanced Breast Cancer From SOLAR-1
Abstract
Purpose: In the phase III SOLAR-1 trial (NCT02437318), the PI3Kα-selective inhibitor and degrader alpelisib significantly improved median progression-free survival when added to fulvestrant in patients with phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha (PIK3CA)-mutated, hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer. We assessed health-related quality of life using patient-reported outcome measures in these patients.
Materials and methods: In the PIK3CA-mutant cohort, 341 patients were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive alpelisib 300 mg daily or placebo plus fulvestrant 500 mg on days 1 and 15 of cycle 1 and on day 1 of subsequent 28-day cycles. Patient-reported outcomes were evaluated with the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer QoL of Cancer Patients and Brief Pain Inventory-Short Form questionnaires. Changes from baseline and time to 10% deterioration were analyzed using repeated measurement models and Cox models, respectively.
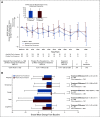
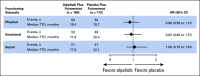
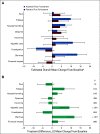
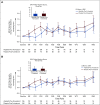
Results: Global Health Status/QoL and functional status were maintained from baseline (mean changes < 10 points) in the alpelisib (overall change from baseline [95% CI], -3.50 [-8.02 to 1.02]) and placebo arms (overall change from baseline [95% CI], 0.27 [-4.48 to 5.02]). Overall treatment effect in Global Health Status/QoL was not significantly different between arms (-3.77; 95% CI, -8.35 to 0.80; P = .101). Time to 10% deterioration for Global Health Status/QoL was similar between arms (hazard ratio, 1.03; 95% CI, 0.72 to 1.48). Compared with placebo, deterioration in social functioning and in diarrhea, appetite loss, nausea or vomiting, and fatigue symptom subscales occurred with alpelisib. Numerical improvement in Worst Pain was observed with alpelisib versus placebo (42% v 32%, week 24; P = .090).
Conclusion: In SOLAR-1, there was no statistical difference in deterioration of Global Health Status/QoL between arms, whereas symptom subscales favored placebo for diarrhea, appetite loss, nausea or vomiting, and fatigue, known side effects of alpelisib. Treatment decisions must consider efficacy and tolerability; taken with clinical efficacy, these results support the benefit-risk profile of alpelisib in patients with hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative PIK3CA-mutated advanced breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Andre F Ciruelos E Rubovszky G, et al. : Alpelisib for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med 380:1929-1940, 2019 - PubMed
-
- Rugo HS Rumble RB Macrae E, et al. : Endocrine therapy for hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology guideline. J Clin Oncol 34:3069-3103, 2016 - PubMed
-
- Slamon DJ Neven P Chia S, et al. : Phase III randomized study of ribociclib and fulvestrant in hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer: MONALEESA-3. J Clin Oncol 36:2465-2472, 2018 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

