Aerosol 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 supplementation: A strategy to boost anti-tumor innate immune activity
- PMID: 33780475
- PMCID: PMC8007042
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248789
Aerosol 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 supplementation: A strategy to boost anti-tumor innate immune activity
Abstract
Background: 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 [1,25(OH)2D3] plays a role in calcium homeostasis but can also exert immunomodulatory effects. In lungs, characterized by a particular immunosuppressive environment primarily due to the presence of alveolar macrophages (AM), 1,25(OH)2D3 has been shown to favor the immune response against pathogens. Here, we explored the ability of aerosolized 1,25(OH)2D3 to locally promote an anti-tumor phenotype in alveolar macrophages (AM) in the treatment of lung metastases.
Methods: Cytotoxicity assay has been used to assess the capability of AM, in vitro treated of not with 1,25(OH)2D3, to stimulate NK cells. Sulforhodamine B (SRB) assay has been used to assess the effect of 1,25(OH)2D3 on MC-38 and B16 tumor cells in vitro growth. 1,25(OH)2D3 was aerosolized in immunocompetent mouse models to evaluate the effect of local administration of 1,25(OH)2D3 on in vivo growth of MC-38 and B16 tumor cells within lungs and on infiltrating immune cells.
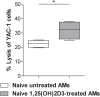
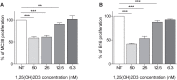
Results: In vitro incubation of naïve AM with 1,25(OH)2D3 improved their ability to stimulate NK cell cytotoxicity. In vivo aerosolized 1,25(OH)2D3 significantly reduced the metastatic growth of MC-38 colon carcinoma, a tumor histotype that frequently metastasizes to lung in human. Immune infiltrate obtained from digested lungs of 1,25(OH)2D3-treated mice bearing MC-38 metastases revealed an increased expression of MHCII and CD80 on AM and an up-modulation of CD69 expression on effector cells that paralleled a strong increased ability of these cells to kill MC-38 tumor in vitro.
Conclusions: Together, these data show that aerosol delivery can represent a feasible and novel approach to supplement 1,25(OH)2D3 directly to the lungs promoting the activation of local immunity against cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

