Reversion inducing cysteine rich protein with Kazal motifs and cardiovascular diseases: The RECKlessness of adverse remodeling
- PMID: 33781845
- PMCID: PMC8204737
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.109993
Reversion inducing cysteine rich protein with Kazal motifs and cardiovascular diseases: The RECKlessness of adverse remodeling
Abstract
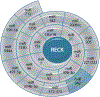
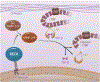
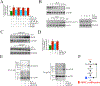
The Reversion Inducing Cysteine Rich Protein With Kazal Motifs (RECK) is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchored membrane-bound regulator of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). It is expressed throughout the body and plays a role in extracellular matrix (ECM) homeostasis and inflammation. In initial studies, RECK expression was found to be downregulated in various invasive cancers and associated with poor prognostic outcome. Restoring RECK, however, has been shown to reverse the metastatic phenotype. Downregulation of RECK expression is also reported in non-malignant diseases, such as periodontal disease, renal fibrosis, and myocardial fibrosis. As such, RECK induction has therapeutic potential in several chronic diseases. Mechanistically, RECK negatively regulates various matrixins involved in cell migration, proliferation, and adverse remodeling by targeting the expression and/or activation of multiple MMPs, A Disintegrin And Metalloproteinase Domain-Containing Proteins (ADAMs), and A Disintegrin And Metalloproteinase With Thrombospondin Motifs (ADAMTS). Outside of its role in remodeling, RECK has also been reported to exert anti-inflammatory effects. In cardiac diseases, for example, it has been shown to counteract several downstream effectors of Angiotensin II (Ang-II) that play a role in adverse cardiac and vascular remodeling, such as Interleukin-6 (IL-6)/IL-6 receptor (IL-6R)/glycoprotein 130 (IL-6 signal transducer) signaling and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) transactivation. This review article focuses on the current understanding of the multifunctional effects of RECK and how its downregulation may contribute to adverse cardiovascular remodeling.
Keywords: Adverse remodeling; EGFR; Fibrosis; Inflammation; Metallopeptidases; RECK.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
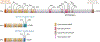



References
-
- Hinz B, The extracellular matrix and transforming growth factor-β1: Tale of a strained relationship, Matrix Biology 47 (2015) 54–65. - PubMed
-
- Briet M, Schiffrin EL, Treatment of Arterial Remodeling in Essential Hypertension, Current Hypertension Reports 15(1) (2013) 3–9. - PubMed
-
- Li L, Zhao Q, Kong W, Extracellular matrix remodeling and cardiac fibrosis, Matrix Biology 68–69 (2018) 490–506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

