Analyzing Possible Native Functions of the Quinolone Resistance Gene qnr in Vibrio vulnificus
- PMID: 33782008
- PMCID: PMC8316120
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00232-21
Analyzing Possible Native Functions of the Quinolone Resistance Gene qnr in Vibrio vulnificus
Abstract
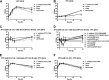
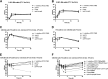
The worldwide distribution of qnr genes found on plasmids and their presence on the chromosomes of aquatic bacteria, such as Vibrio vulnificus, one of the suspected sources, suggests an origin before the development of synthetic quinolones. However, their native function remains unknown. Previous work indicated that expression of qnrVv in V. vulnificus was induced by cold shock. To investigate its role further, we constructed single in-frame deletion mutants in qnrVv and cspA (the gene for cold shock protein) and a double mutant in qnrVv and cspA in V. vulnificus ATCC 17562 to evaluate the response to different environmental conditions and stresses and to exposure to various DNA-damaging agents. We found that qnrVv is involved in resistance to ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, and mitomycin C and in the cold shock response in V. vulnificus Moreover, ΔqnrVv and ΔcspA mutants showed slower growth when they were treated with bile salts at 37°C and then shifted to 15°C (cold shock) without bile salts in the medium, with the effect being stronger in the double mutant. This transition may mimic what happens when V. vulnificus is ingested into the gastrointestinal tract and released in its natural environment. Cold shock and bile salts induced the expression of cspA and DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV genes. However, no induction was found in the ΔqnrVv mutant, suggesting that the qnrVv gene is involved in the response to DNA damage and nucleic acid secondary structure.
Keywords: Qnr; Vibrio vulnificus; bile salts; cold shock; quinolones.
Copyright © 2021 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cold shock induces chromosomal qnr in Vibrio species and plasmid-mediated qnrS1 in Escherichia coli.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Sep 9;63(12):e01472-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01472-19. Epub 2019 Sep 30. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 31570402 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous quinolone resistance in the zoonotic serovar of Vibrio vulnificus.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009 Apr;75(8):2577-80. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02921-08. Epub 2009 Feb 13. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19218407 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Apr 16;99(8):5638-42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.082092899. Epub 2002 Apr 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 11943863 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of drug resistance: quinolone resistance.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015 Sep;1354(1):12-31. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12830. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015. PMID: 26190223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Mechanisms of plasmid-mediated resistance to quinolones].Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2005 Jan;23(1):25-31. doi: 10.1157/13070406. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2005. PMID: 15701330 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Genome analysis of clinical genotype Vibrio vulnificus isolated from seafood in Mangaluru Coast, India provides insights into its pathogenicity.Vet Q. 2023 Dec;43(1):1-17. doi: 10.1080/01652176.2023.2240389. Vet Q. 2023. PMID: 37478018 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

