Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection with LamPORE, a High-Throughput Platform Combining Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification and Nanopore Sequencing
- PMID: 33782112
- PMCID: PMC8315953
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.03271-20
Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection with LamPORE, a High-Throughput Platform Combining Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification and Nanopore Sequencing
Abstract
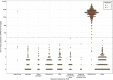
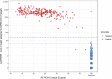
LamPORE is a novel diagnostic platform for the detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) RNA combining loop-mediated isothermal amplification with nanopore sequencing, which could potentially be used to analyze thousands of samples per day on a single instrument. We evaluated the performance of LamPORE against reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) using RNA extracted from spiked respiratory samples and stored nose and throat swabs collected at two UK hospitals. The limit of detection of LamPORE was 10 genome copies/μl of extracted RNA, which is above the limit achievable by RT-PCR, but was not associated with a significant reduction of sensitivity in clinical samples. Positive clinical specimens came mostly from patients with acute symptomatic infection, and among them, LamPORE had a diagnostic sensitivity of 99.1% (226/228; 95% confidence interval [CI], 96.9% to 99.9%). Among negative clinical specimens, including 153 with other respiratory pathogens detected, LamPORE had a diagnostic specificity of 99.6% (278/279; 98.0% to 100.0%). Overall, 1.4% (7/514; 0.5% to 2.9%) of samples produced an indeterminate result on first testing, and repeat LamPORE testing on the same RNA extract had a reproducibility of 96.8% (478/494; 94.8% to 98.1%). LamPORE has a similar performance as RT-PCR for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection in symptomatic patients and offers a promising approach to high-throughput testing.
Keywords: LamPORE; SARS-CoV-2; diagnosis; nanopore sequencing.
Copyright © 2021 Peto et al.
Figures
References
-
- Grassly NC, Pons-Salort M, Parker EPK, White PJ, Ferguson NM, Ainslie K, Baguelin M, Bhatt S, Boonyasiri A, Brazeau N, Cattarino L, Coupland H, Cucunuba Z, Cuomo-Dannenburg G, Dighe A, Donnelly C, van Elsland SL, FitzJohn R, Flaxman S, Fraser K, Gaythorpe K, Green W, Hamlet A, Hinsley W, Imai N, Knock E, Laydon D, Mellan T, Mishra S, Nedjati-Gilani G, Nouvellet P, Okell L, Ragonnet-Cronin M, Thompson HA, Unwin HJT, Vollmer M, Volz E, Walters C, Wang Y, Watson OJ, Whittaker C, Whittles L, Xi X. 2020. Comparison of molecular testing strategies for COVID-19 control: a mathematical modelling study. Lancet Infect Dis 20:1381–1389. 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30630-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Peto J, Carpenter J, Smith GD, Duffy S, Houlston R, Hunter DJ, McPherson K, Pearce N, Romer P, Sasieni P, Turnbull C. 2020. Weekly COVID-19 testing with household quarantine and contact tracing is feasible and would probably end the epidemic. R Soc Open Sci 7:200915. 10.1098/rsos.200915. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fowler VL, Armson B, Gonzales JL, Wise EL, Howson ELA, Vincent-Mistiaen Z, Fouch S, Maltby CJ, Grippon S, Munro S, Jones L, Holmes T, Tillyer C, Elwell J, Sowood A, de Peyer O, Dixon S, Hatcher T, Patrick H, Laxman S, Walsh C, Andreou M, Morant N, Clark D, Moore N, Houghton R, Cortes NJ, Kidd SP. 2021. A highly effective reverse-transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) assay for the rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection. J Infect 82:117–125. 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.10.039. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez-Manzano J, Malpartida-Cardenas K, Moser N, Pennisi I, Cavuto M, Miglietta L, Moniri A, Penn R, Satta G, Randell P, Davies F, Bolt F, Barclay W, Holmes A, Georgiou P. 2021. Handheld point-of-care system for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 extracted RNA in under 20 min. ACS Cent Sci 7:307–317. 10.1021/acscentsci.0c01288. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- James P, Stoddart D, Harrington ED, Beaulaurier J, Ly L, Reid SW, Turner DJ, Juul S. 2020. LamPORE: rapid, accurate and highly scalable molecular screening for SARS-CoV-2 infection, based on nanopore sequencing. medRxiv 10.1101/2020.08.07.20161737. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

