Profiling PRMT methylome reveals roles of hnRNPA1 arginine methylation in RNA splicing and cell growth
- PMID: 33782401
- PMCID: PMC8007824
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-21963-1
Profiling PRMT methylome reveals roles of hnRNPA1 arginine methylation in RNA splicing and cell growth
Abstract
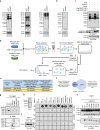
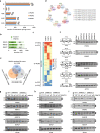
Numerous substrates have been identified for Type I and II arginine methyltransferases (PRMTs). However, the full substrate spectrum of the only type III PRMT, PRMT7, and its connection to type I and II PRMT substrates remains unknown. Here, we use mass spectrometry to reveal features of PRMT7-regulated methylation. We find that PRMT7 predominantly methylates a glycine and arginine motif; multiple PRMT7-regulated arginine methylation sites are close to phosphorylations sites; methylation sites and proximal sequences are vulnerable to cancer mutations; and methylation is enriched in proteins associated with spliceosome and RNA-related pathways. We show that PRMT4/5/7-mediated arginine methylation regulates hnRNPA1 binding to RNA and several alternative splicing events. In breast, colorectal and prostate cancer cells, PRMT4/5/7 are upregulated and associated with high levels of hnRNPA1 arginine methylation and aberrant alternative splicing. Pharmacological inhibition of PRMT4/5/7 suppresses cancer cell growth and their co-inhibition shows synergistic effects, suggesting them as targets for cancer therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Jarrold, J. & Davies, C. C. PRMTs and Arginine methylation: cancer’s best-kept secret? Trends Mol. Med. 10.1016/j.molmed.2019.05.007 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

