In vivo self-assembled small RNAs as a new generation of RNAi therapeutics
- PMID: 33782530
- PMCID: PMC8169669
- DOI: 10.1038/s41422-021-00491-z
In vivo self-assembled small RNAs as a new generation of RNAi therapeutics
Abstract
RNAi therapy has undergone two stages of development, direct injection of synthetic siRNAs and delivery with artificial vehicles or conjugated ligands; both have not solved the problem of efficient in vivo siRNA delivery. Here, we present a proof-of-principle strategy that reprogrammes host liver with genetic circuits to direct the synthesis and self-assembly of siRNAs into secretory exosomes and facilitate the in vivo delivery of siRNAs through circulating exosomes. By combination of different genetic circuit modules, in vivo assembled siRNAs are systematically distributed to multiple tissues or targeted to specific tissues (e.g., brain), inducing potent target gene silencing in these tissues. The therapeutic value of our strategy is demonstrated by programmed silencing of critical targets associated with various diseases, including EGFR/KRAS in lung cancer, EGFR/TNC in glioblastoma and PTP1B in obesity. Overall, our strategy represents a next generation RNAi therapeutics, which makes RNAi therapy feasible.
Conflict of interest statement
C.-Y.Z., X.C. and H.L. are co-inventors on patents related to using the genetic circuits to treat diseases. The application numbers are PCT/CN2015/094809, PCT/CN2017/083311 and PCT/CN2017/083312. K.Z. is a co-inventor on PCT/CN2015/094809 and PCT/CN2017/083311. U.U.-R. is a co-inventor on PCT/CN2017/083311 and PCT/CN2017/083312.
Figures
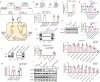
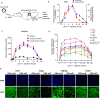
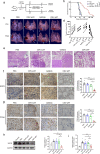
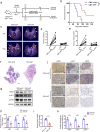
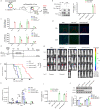
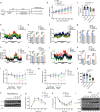
References
-
- Bobbin ML, Rossi JJ. RNA interference (RNAi)-based therapeutics: delivering on the promise? Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016;56:103–122. - PubMed
-
- Singh A, Trivedi P, Jain NK. Advances in siRNA delivery in cancer therapy. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018;46:274–283. - PubMed
-
- Nair JK, et al. Multivalent N-acetylgalactosamine-conjugated siRNA localizes in hepatocytes and elicits robust RNAi-mediated gene silencing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014;136:16958–16961. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

