Isorhamnetin Ameliorates Aspergillus fumigatus Keratitis by Reducing Fungal Load, Inhibiting Pattern-Recognition Receptors and Inflammatory Cytokines
- PMID: 33783487
- PMCID: PMC8010362
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.62.3.38
Isorhamnetin Ameliorates Aspergillus fumigatus Keratitis by Reducing Fungal Load, Inhibiting Pattern-Recognition Receptors and Inflammatory Cytokines
Abstract
Purpose: Isorhamnetin is a natural flavonoid with both antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, but its effect on fungal keratitis (FK) remains unknown. The current study aims to investigate the antifungal and anti-inflammatory effects of isorhamnetin against mouse Aspergillus fumigatus keratitis.
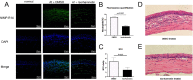
Methods: In vitro, the lowest effective concentration of isorhamnetin was assessed by minimum inhibitory concentration and cytotoxicity tests in human corneal epithelial cells (HCECs) and RAW264.7 cells. The antifungal property was investigated by scanning electron microscopy and propidium iodide uptake test. The anti-inflammatory effect of isorhamnetin in HCECs and RAW264.7 cells was observed by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). In the eyes of mice with A. fumigatus keratitis, FK severity was evaluated using clinical score, plate counting, histological staining and periodic acid Schiff staining. In vivo, the anti-inflammatory effect of isorhamnetin was examined by immunofluorescence staining, myeloperoxidase assay, Western blot, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and qRT-PCR.
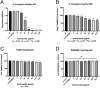
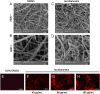
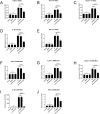
Results: In HCECs and RAW264.7 cells, isorhamnetin significantly inhibited A. fumigatus conidia growth and hyphae viability at 80 µg/mL without affecting cell viability. In vitro, isorhamnetin altered A. fumigatus hyphal morphology and membrane integrity. In A. fumigatus keratitis mouse model, isorhamnetin treatment alleviated the severity of FK by reducing corneal fungal load and inhibiting neutrophil recruitment. In addition, the mRNA and protein expression levels of TLR-2, TLR-4, Dectin-1, IL-1β, and tumor necrosis factor-α were significantly decreased in isorhamnetin-treated groups in vivo and in vitro.
Conclusions: Isorhamnetin improves the prognosis of A. fumigatus keratitis in mice by inhibiting the growth of A. fumigatus, reducing the recruitment of neutrophils and downregulating inflammatory factors.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures

References
-
- Huang JF, Zhong J, Chen GP, et al. .. A Hydrogel-Based Hybrid Theranostic Contact Lens for Fungal Keratitis. ACS Nano. 2016; 10: 6464–6473. - PubMed
-
- Kredics L, Narendran V, Shobana CS, et al. .. Filamentous fungal infections of the cornea: a global overview of epidemiology and drug sensitivity. Mycoses . 2015; 58: 243–260. - PubMed
-
- Tabatabaei SA, Soleimani M, Tabatabaei SM, et al. .. The use of in vivo confocal microscopy to track treatment success in fungal keratitis and to differentiate between Fusarium and Aspergillus keratitis. Int Ophthalmol. 2020; 40: 483–449. - PubMed
-
- Aveyard J, Deller RC, Lace R, et al. .. Antimicrobial Nitric Oxide Releasing Contact Lens Gels for the Treatment of Microbial Keratitis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019; 11: 37491–37501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

