One Year Real-World Use of the Control-IQ Advanced Hybrid Closed-Loop Technology
- PMID: 33784196
- PMCID: PMC8501470
- DOI: 10.1089/dia.2021.0097
One Year Real-World Use of the Control-IQ Advanced Hybrid Closed-Loop Technology
Abstract
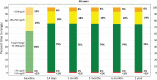
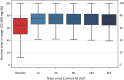
Background: The t:slim X2™ insulin pump with Control-IQ® technology from Tandem Diabetes Care is an advanced hybrid closed-loop system that was first commercialized in the United States in January 2020. Longitudinal glycemic outcomes associated with real-world use of this system have yet to be reported. Methods: A retrospective analysis of Control-IQ technology users who uploaded data to Tandem's t:connect® web application as of February 11, 2021 was performed. Users age ≥6 years, with >2 weeks of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data pre- and >12 months post-Control-IQ technology initiation were included in the analysis. Results: In total 9451 users met the inclusion criteria, 83% had type 1 diabetes, and the rest had type 2 or other forms of diabetes. The mean age was 42.6 ± 20.8 years, and 52% were female. Median percent time in automation was 94.2% [interquartile range, IQR: 90.1%-96.4%] for the entire 12-month duration of observation, with no significant changes over time. Of these users, 9010 (96.8%) had ≥75% of their CGM data available, that is, sufficient data for reliable computation of CGM-based glycemic outcomes. At baseline, median percent time in range (70-180 mg/dL) was 63.6 (IQR: 49.9%-75.6%) and increased to 73.6% (IQR: 64.4%-81.8%) for the 12 months of Control-IQ technology use with no significant changes over time. Median percent time <70 mg/dL remained consistent at ∼1% (IQR: 0.5%-1.9%). Conclusion: In this real-world use analysis, Control-IQ technology retained, and to some extent exceeded, the results obtained in randomized controlled trials, showing glycemic improvements in a broad age range of people with different types of diabetes.
Keywords: Automated insulin dosing; Closed-loop control; Continuous glucose monitoring; Time in range.
Conflict of interest statement
M.D.B. reports research support from Dexcom, Inc., Arecor Ltd., Novo Nordisk A/S, and Tandem Diabetes Care, Inc; M.D.B. reports consulting fees from Dexcom, Inc., Arecor, and Adocia. B.P.K. reports research support handled by the University of Virginia from Dexcom, Inc., Novo Nordisk A/S, and Tandem Diabetes Care, Inc; M.D.B. and B.P.K. report patent royalties, managed by the University of Virginia, from Johnson & Johnson, Sanofi, and Dexcom.
Figures




References
-
- Kovatchev BP: A century of diabetes technology: signals, models, and artificial pancreas control. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2019;30:432–444 - PubMed
-
- Hovorka R, Chassin LJ, Wilinska ME, et al. : Closing the loop: the ADICOL experience. Diabetes Technol Ther 2004;6:307–318 - PubMed
-
- Steil GM, Rebrin K, Darwin C, et al. : Feasibility of automating insulin delivery for the treatment of Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes 2006;55:3344–3350 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

