Circulating plasma microRNAs in systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 33784391
- PMCID: PMC8742821
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab300
Circulating plasma microRNAs in systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
Objectives: SSc-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension (SSc-APAH) is a late but devastating complication of SSc. Early identification of SSc-APAH may improve survival. We examined the role of circulating miRNAs in SSc-APAH.
Methods: Using quantitative RT-PCR the abundance of mature miRNAs in plasma was determined in 85 female patients with ACA-positive lcSSc. Twenty-two of the patients had SSc-APAH. Sixty-three SSc controls without PAH were matched for disease duration. Forty-six selected miRNA plasma levels were correlated with clinical data. Longitudinal samples were analysed from 14 SSc-APAH and 27 SSc patients.
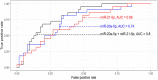
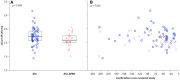
Results: The disease duration was 12 years for the SSc-APAH patients and 12.7 years for the SSc controls. Plasma expression levels of 11 miRNAs were lower in patients with SSc-APAH. Four miRNAs displayed higher plasma levels in SSc-APAH patients compared with SSc controls. There was significant difference between groups for miR-20a-5p and miR-203a-3p when correcting for multiple comparisons (P = 0.002 for both). Receiver operating characteristics curve showed AUC = 0.69-0.83 for miR-21-5p and miR-20a-5p or their combination. miR-20a-5p and miR-203a-3p correlated inversely with NT-pro-Brain Natriuretic Protein levels (r = -0.42 and -0.47). Mixed effect model analysis could not identify any miRNAs as predictor of PAH development. However, miR-20a-5p plasma levels were lower in the longitudinal samples of SSc-APAH patients than in the SSc controls.
Conclusions: Our study links expression levels of the circulating plasma miRNAs, especially miR-20a-5p and miR-203a-3p, to the occurrence of SSc-APAH in female patients with ACA-positive lcSSc.
Keywords: NT-pro-Brain Natriuretic Protein; microRNA; pulmonary arterial hypertension; systemic sclerosis.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures


References
-
- Semalulu T, Rudski L, Huynh T. et al. An evidence-based strategy to screen for pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic sclerosis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2020; 50:1421–7. - PubMed
-
- Steen VD. Autoantibodies in systemic sclerosis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2005;35:35–42. - PubMed
-
- Mihai C, Landewé R, van der Heijde D et al.; EUSTAR co-authors. Digital ulcers predict a worse disease course in patients with systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 2016;75:681–6. - PubMed
-
- Hesselstrand R, Wildt M, Ekmehag B, Wuttge DM, Scheja A.. Survival in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with systemic sclerosis from a Swedish single centre: prognosis still poor and prediction difficult. Scand J Rheumatol 2011;40:127–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

