Phase I Study of Zotiraciclib in Combination with Temozolomide for Patients with Recurrent High-grade Astrocytomas
- PMID: 33785481
- PMCID: PMC8197750
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-4730
Phase I Study of Zotiraciclib in Combination with Temozolomide for Patients with Recurrent High-grade Astrocytomas
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the toxicity profile and establish an optimal dosing schedule of zotiraciclib with temozolomide in patients with recurrent high-grade astrocytoma.
Patients and methods: This two-stage phase I trial determined the MTD of zotiraciclib combined with either dose-dense (Arm1) or metronomic (Arm2) temozolomide using a Bayesian Optimal Interval design; then a randomized cohort expansion compared the progression-free survival rate at 4 months (PFS4) of the two arms for an efficient determination of a temozolomide schedule to combine with zotiraciclib at MTD. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacogenomic profiling were included. Patient-reported outcome was evaluated by longitudinal symptom burden.
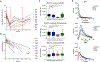
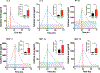
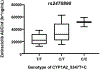
Results: Fifty-three patients were enrolled. Dose-limiting toxicities were neutropenia, diarrhea, elevated liver enzymes, and fatigue. MTD of zotiraciclib was 250 mg in both arms and thus selected for the cohort expansion. Dose-dense temozolomide plus zotiraciclib (PSF4 40%) compared favorably with metronomic temozolomide (PFS4 25%). Symptom burden worsened at cycle 2 but stabilized by cycle 4 in both arms. A significant decrease in absolute neutrophil count and neutrophil reactive oxygen species production occurred 12-24 hours after an oral dose of zotiraciclib but both recovered by 72 hours. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacogenomic analyses revealed that the CYP1A2_5347T>C (rs2470890) polymorphism was associated with higher AUCinf value.
Conclusions: Zotiraciclib combined with temozolomide is safe in patients with recurrent high-grade astrocytomas. Zotiraciclib-induced neutropenia can be profound but mostly transient, warranting close monitoring rather than treatment discontinuation. Once validated, polymorphisms predicting drug metabolism may allow personalized dosing of zotiraciclib.
©2021 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest:
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 2005;352(10):987–96. - PubMed
-
- Wong ET, Hess KR, Gleason MJ, Jaeckle KA, Kyritsis AP, Prados MD, et al. Outcomes and prognostic factors in recurrent glioma patients enrolled onto phase II clinical trials. J Clin Oncol 1999;17(8):2572–8. - PubMed
-
- Goh KC, Novotny-Diermayr V, Hart S, Ong LC, Loh YK, Cheong A, et al. TG02, a novel oral multi-kinase inhibitor of CDKs, JAK2 and FLT3 with potent anti-leukemic properties. Leukemia 2012;26(2):236–43. - PubMed

