Computerized image understanding system for reliable estimation of spinal curvature in idiopathic scoliosis
- PMID: 33785803
- PMCID: PMC8009897
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-86436-3
Computerized image understanding system for reliable estimation of spinal curvature in idiopathic scoliosis
Abstract
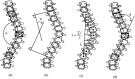
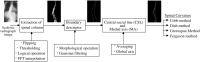
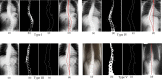
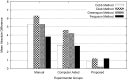
Analysis of scoliosis requires thorough radiographic evaluation by spinal curvature estimation to completely assess the spinal deformity. Spinal curvature estimation gives orthopaedic surgeons an idea of severity of spinal deformity for therapeutic purposes. Manual intervention has always been an issue to ensure accuracy and repeatability. Computer assisted systems are semi-automatic and is still influenced by surgeon's expertise. Spinal curvature estimation completely relies on accurate identification of required end vertebrae like superior end-vertebra, inferior end-vertebra and apical vertebra. In the present work, automatic extraction of spinal information central sacral line and medial axis by computerized image understanding system has been proposed. The inter-observer variability in the anatomical landmark identification is quantified using Kappa statistic. The resultant Kappa value computed between proposed algorithm and observer lies in the range 0.7 and 0.9, which shows good accuracy. Identification of the required end vertebra is automated by the extracted spinal information. Difference in inter and intra-observer variability for the state of the art computer assisted and proposed system are quantified in terms of mean absolute difference for the various types (Type-I, Type-II, Type-III, Type-IV, and Type-V) of scoliosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Automated comprehensive Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis assessment using MVC-Net.Med Image Anal. 2018 Aug;48:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2018.05.005. Epub 2018 May 18. Med Image Anal. 2018. PMID: 29803920
-
Cobb Angle Measurement of Spine from X-Ray Images Using Convolutional Neural Network.Comput Math Methods Med. 2019 Feb 19;2019:6357171. doi: 10.1155/2019/6357171. eCollection 2019. Comput Math Methods Med. 2019. PMID: 30996731 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical validation of coronal and sagittal spinal curve measurements based on three-dimensional vertebra vector parameters.Spine J. 2012 Oct;12(10):960-8. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2012.08.175. Epub 2012 Sep 24. Spine J. 2012. PMID: 23018164
-
Evaluation and comparison of accurate automated spinal curvature estimation algorithms with spinal anterior-posterior X-Ray images: The AASCE2019 challenge.Med Image Anal. 2021 Aug;72:102115. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2021.102115. Epub 2021 Jun 1. Med Image Anal. 2021. PMID: 34134084 Review.
-
Radiographic methods to estimate surgical outcomes based on spinal flexibility assessment in patients who have adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A systematic review.Spine J. 2018 Nov;18(11):2128-2139. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2018.06.344. Epub 2018 Jun 26. Spine J. 2018. PMID: 29959103
Cited by
-
Application of machine learning standardized integral area algorithm in measuring the scoliosis.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 7;13(1):19255. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-44252-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37935731 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Mis-Selection of End Vertebrae and Its Effect on Measuring Cobb Angle and Curve Length in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 5;13(15):4562. doi: 10.3390/jcm13154562. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39124828 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging Methods to Quantify the Chest and Trunk Deformation in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Literature Review.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 May 19;11(10):1489. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11101489. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37239775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Convolutional Neural Network-Based Approach for Cobb Angle Measurement Using Mask R-CNN.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Apr 23;15(9):1066. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15091066. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40361884 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

