Incidence, Risk-Factors and Associated Mortality of Complications in Orthogeriatric Co-Managed Inpatients
- PMID: 33786204
- PMCID: PMC7961710
- DOI: 10.1177/2151459321998314
Incidence, Risk-Factors and Associated Mortality of Complications in Orthogeriatric Co-Managed Inpatients
Abstract
Introduction: Pneumonia, thromboembolic and ischemic events, urinary tract infections (UTI), delirium and acute kidney injury (AKI) are common complications during the treatment of fragility fractures. In a 2 years-follow-up we determined the according incidence and risk factors of these and other complications in orthogeriatric inward patients, as well as the respective associated mortality.
Methods: All patients treated on an orthogeriatric co-managed ward over the course of a year were included. Besides injury, therapy and geriatric assessment parameters, we evaluated the inward incidence of common complications. In a 2 years-follow-up the associated death rates were aquired. SPSS (IBM) was used to determine the importance of risk factors predisposing to the respective occurrence of a complication and accordingly determine it's impact on the patients' 1- and 2-years-mortality.
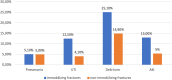
Results: 830 orthogeriatric patients were initially assessed with a remaining follow-up cohort of 661 (79.6%). We observed very few cases of thrombosis (0.6%), pulmonary embolism (0.5%), apoplex (0.5%) and myocardial infarction (0.8%). Pneumonia was seen in 42 (5.1%), UTI in 85 (10.2%), delirium in 186 (22.4%) and AKI in 91 (11.0%) patients. Consistently ADL on admission was found to be a relevant risk factor in the development of each complication. After adjustment only AKI showed a significant increased mortality risk of 1.60 (95%CI:1.086-2.350).
Discussion: In our fracture-independent assessment of complications in the orthogeriatric treatment of inward patients we've seen very rare cases of cardiac and thrombotic complications. Typical fragility-fracture associated common events like pneumonia, UTI, delirium and AKI were still more incidental. No complication except AKI was associated to significant increased mortality risk.
Conclusions: The relevance of orthogeriatric care in prevention and outcome of inward complications seems promising, needing still more controlled studies, evaluating not just hip fracture patients but more diverse groups. Consensus is needed in the scholar evaluation of orthogeriatric complications.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; complication; delirium; fragility fractures; immobility; mortality; orthogeriatric comanagement; pneumonia; risk factors.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Complications during hospitalization and risk factors in elderly patients with hip fracture following integrated orthogeriatric treatment.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017 Apr;137(4):507-515. doi: 10.1007/s00402-017-2646-6. Epub 2017 Feb 23. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017. PMID: 28233062
-
Orthogeriatric co-management improves the outcome of long-term care residents with fragility fractures.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2016 Oct;136(10):1403-9. doi: 10.1007/s00402-016-2543-4. Epub 2016 Aug 8. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2016. PMID: 27501701 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Prognostic value of orthogeriatric assessment parameters on mortality: a 2-year follow-up.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2022 Aug;48(4):2905-2914. doi: 10.1007/s00068-021-01727-8. Epub 2021 Jun 25. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2022. PMID: 34173021 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying a standard set of outcome parameters for the evaluation of orthogeriatric co-management for hip fractures.Injury. 2013 Nov;44(11):1403-12. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2013.06.018. Epub 2013 Jul 21. Injury. 2013. PMID: 23880377 Review.
-
Orthogeriatrics in the management of frail older patients with a fragility fracture.Osteoporos Int. 2015 Oct;26(10):2387-99. doi: 10.1007/s00198-015-3166-2. Epub 2015 May 19. Osteoporos Int. 2015. PMID: 25986384 Review.
Cited by
-
Factors involved in the development of hospital-acquired conditions in older patients in acute care settings: a scoping review.BMC Health Serv Res. 2025 Jan 29;25(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s12913-025-12318-3. BMC Health Serv Res. 2025. PMID: 39881323 Free PMC article.
-
Orthogeriatric Assessment of the Elderly Patient with Fragility Hip Fracture: Preliminary Results of a Prospective Study.J Pers Med. 2023 Jul 14;13(7):1138. doi: 10.3390/jpm13071138. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37511751 Free PMC article.
-
Functional autonomy and 12-month mortality in older adults with proximal femoral fractures in an orthogeriatric setting: risk factors and gender differences.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2023 May;35(5):1063-1071. doi: 10.1007/s40520-023-02378-y. Epub 2023 Mar 9. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2023. PMID: 36892795
-
Comparison of two surgical treatment strategies for fragility fractures of the pelvis based on early postoperative mobility outcomes using insole force sensors.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024 Dec 16;145(1):50. doi: 10.1007/s00402-024-05707-6. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024. PMID: 39680154
-
Risk factors for urinary tract infection in geriatric hip fracture patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Feb 9;11:1360058. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1360058. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38405191 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Friedman SM, Mendelson DA. Epidemiology of fragility fractures, Vol. 30. Clin Geriatr Med. 2014;30(2):175–181. - PubMed
-
- Hernlund E, Svedbom A, Ivergård M, et al. Osteoporosis in the European Union: medical management, epidemiology and economic burden: a report prepared in collaboration with the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) and the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industry Associations (EFPIA). Arch Osteoporos. 2013;8(1-2):136. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cooper C, Atkinson EJ, Jacobsen SJ, O’fallon WM, Melton LJ. Population-based study of survival after osteoporotic fractures. Am J Epidemiol. 1993;137(9):1001–1005. - PubMed
-
- Kim JY, Yoo JH, Kim E, et al. Risk factors and clinical outcomes of delirium in osteoporotic hip fractures. J Orthop Surg. 2017;25(3):2309499017739485. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources