Partial Single Stage Exchange Arthroplasty With Retention of a Well Fixed Cemented Femoral Stem for the Treatment of Culture Negative Infection in a Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty: A Case Report
- PMID: 33786206
- PMCID: PMC7961682
- DOI: 10.1177/21514593211001844
Partial Single Stage Exchange Arthroplasty With Retention of a Well Fixed Cemented Femoral Stem for the Treatment of Culture Negative Infection in a Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty: A Case Report
Abstract
Background: Prosthetic joint infection (PJI) is the second most common cause for revision following hip hemiarthroplasty (HHA) resulting in a mortality rate of 5.6%. The treatment of PJI is both challenging and controversial, without general consensus on best practice. In an attempt to avoid surgery, patients are commonly prescribed antibiotics, reducing the chance of detecting a microorganism, and culture negative infections are reported to occur in up to 21% of all PJI. Two stage revision is arguably the gold standard treatment but frequently these patients are too frail to undergo such extensive procedures. Some surgeons have attempted to avoid this by leaving well fixed implants undisturbed, effectively performing a partial single-stage revision.
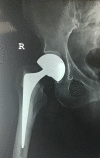
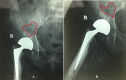
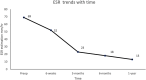
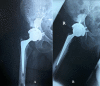
Case presentation: A previously well 83 -year-old female patient presented with a gradual onset of increasing pain and difficulty walking. Just over 1 year prior to this presentation she fell at home and underwent an uncomplicated bipolar hemiarthroplasty. Clinical examination as well as serological and radiological investigations were suspicious for a periprosthetic infection. Her rapidly deteriorating clinical picture required prompt surgical intervention. In theater the patient underwent a single stage partial exchange arthroplasty leaving the well cemented femoral stem undisturbed. Although multiple samples were taken, no microorganism was identified. The patient has been followed up for 1 year and remains well, with no recurrence of infection. Her inflammatory markers have returned to normal and radiographs demonstrate no evidence of loosening of the total hip replacement.
Conclusion: The burden of infection following hip hemiarthroplasty is likely to parallel the predicted increase in hip fractures. The combination of physiologic frailty, osteoporosis and multiple medical comorbidities are pertinent factors for consideration in the development of a treatment strategy. A partial single stage revision THR performed by an experienced arthroplasty surgeon, along with expertly led antimicrobial therapy may be considered in carefully selected patients.
Keywords: culture negative; hip fracture; hip hemiarthroplasty; prosthetic joint infection; single stage revision.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Cooper C, Campion G, Melton LJ, 3rd. Hip fractures in the elderly: a world-wide projection. Osteoporos Int. 1992;2(6):285–289. doi:10.1007/bf01623184 - PubMed
-
- Noailles T, Brulefert K, Chalopin A, Longis PM, Gouin F. What are the risk factors for post-operative infection after hip hemiarthroplasty? Systematic review of literature. Int orthop. 2016;40(9):1843–1848. doi:10.1007/s00264-015-3033-y - PubMed
-
- Ferguson D, Jones S, Parker J, Aderinto J. Outcome of prosthetic infection following hip hemiarthroplasty surgery for intracapsular neck of femur fractures. Orthop Proc. 2013;95-B(Supp 1):91–91. doi:10.1302/1358-992x.95bsupp_1.Boa2012-091
-
- DeLee JG, Charnley J. Radiological demarcation of cemented sockets in total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976;(121):20–32. - PubMed
-
- Lora-Tamayo J, Euba G, Ribera A, et al. Infected hip hemiarthroplasties and total hip arthroplasties: differential findings and prognosis. J Infect. 2013;67(6):536–544. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2013.07.030 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

