Sulfoglycodendrimer Therapeutics for HIV-1 and SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 33786368
- PMCID: PMC7995185
- DOI: 10.1002/adtp.202000210
Sulfoglycodendrimer Therapeutics for HIV-1 and SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
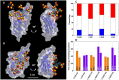
Hexavalent sulfoglycodendrimers (SGDs) are synthesized as mimics of host cell heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) to inhibit the early stages in viral binding/entry of HIV-1 and SARS-CoV-2. Using an HIV neutralization assay, the most promising of the seven candidates are found to have sub-micromolar anti-HIV activities. Molecular dynamics simulations are separately implemented to investigate how/where the SGDs interacted with both pathogens. The simulations revealed that the SGDs: 1) develop multivalent binding with polybasic regions within and outside of the V3 loop on glycoprotein 120 (gp120) for HIV-1, and consecutively bind with multiple gp120 subunits, and 2) interact with basic amino acids in both the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and HSPG binding regions of the Receptor Binding Domain (RBD) from SARS-CoV-2. These results illustrate the considerable potential of SGDs as inhibitors in viral binding/entry of both HIV-1 and SARS-CoV-2 pathogens, leading the way for further development of this class of molecules as broad-spectrum antiviral agents.
Keywords: HIV‐1; SARS‐CoV‐2 receptor binding domain; glycodendrimers; molecular dynamics.
© 2021 Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- UNAIDS, Fact Sheet‐World AIDS Day, https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet (accessed: December 2020).
-
- Worldometer, Coronavirus, https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/ (accessed: December 2020).
-
- CDC, Flu Vaccination Coverage, United States, 2018–19 Influenza Season, https://www.cdc.gov/flu/fluvaxview/coverage-1819estimates.htm (accessed: May 2020).
-
- a) Spillmann D., Biochimie 2001, 83, 811; - PubMed
- b) Choi Y., Chung H., Jung H., Couchman J. R., Oh E.‐S., Matrix Biol. 2011, 30, 93; - PubMed
- c) Kamhi E., Joo E. J., Dordick J. S., Linhardt R. J., Biological Rev. 2013, 88, 928; - PubMed
- d) Chen Y., Gotte M., Liu J., Park P. W., Mol. Cells 2008, 26, 415; - PubMed
- e) Lang J., Yang N., Deng J., Liu K., Yang P., Zhang G., Jiang C., PloS One 2011, 6, e23710; - PMC - PubMed
- f) Hondermarck H., Bartlett N. W., Nurcombe V., FASEB BioAdv. 2020, 2, 296. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
