Formulation and evaluation of mucoadhesive buccal tablets of aceclofenac
- PMID: 33786387
- PMCID: PMC7988282
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06439
Formulation and evaluation of mucoadhesive buccal tablets of aceclofenac
Abstract
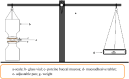
This project was aimed to formulate and characterize mucoadhesive buccal tablets of aceclofenac, utilizing different proportions of three polymers carbopol 934, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, and sodium carboxymethylcellulose. Twelve batches of buccoadhesive aceclofenac were prepared by the direct compression method. The compressed tablets were then evaluated for physicochemical parameters such as hardness, thickness, weight variation, drug content, friability, swelling index, surface pH, and ex vivo mucoadhesion. In vitro dissolution test was conducted for 12 h according to Indian Pharmacopeia 2018, using the rotating paddle method in phosphate buffer of pH 7.4. Physiochemical parameters like weight variation (231.25-268.75 mg), hardness (8.32-11.56 kg), friability (0.04-0.2%), diameter (9.00 mm), thickness (3.8-4.05 mm), and drug content ((97.67-102.25%) were within the acceptable limit as per Indian Pharmacopeia 2018. The swelling index was reported to be in the range of 112.93-450.19%, at 8 h. The surface pHs of all the batches were in between 6.72 to 6.96. The mucoadhesive strengths (40.5-50 g) varied with the change in polymer concentrations especially of carbopol 934. The dissolution profile of all the batches varied greatly, with a maximum release of 109.41% (in batch 12 at 6 h) to a minimum release of 44.82% (in batch 3 at 12 h). Among them, only batch 1 ensured sustained and effective drug release (88.34% at 12 h) with appropriate swelling index (112.93%) and mucoadhesive strength (40 g). Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy analysis showed no evidence of drug excipients interaction. Hence, the results concluded that buccal mucoadhesive aceclofenac tablets can be formulated. Furthermore, the property of the tablet not only depends on the concentration but also the behavior of the polymers used.
Keywords: Aceclofenac; Buccal tablets; Mucoadhesion; Swelling index.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Gandhi A. Mouth dissolving tablets: a new venture in modern formulation technology. Pharma Innov. 2012;1(8):14–31.
-
- Bhowmik D., Chiranjib B., Pankaj K., Chandira R.M. Fast dissolving tablet: an overview. J. Chem. Pharm. 2009;1(1):163–177.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

