An updated protocol for the cost-effective and weekend-free culture of human induced pluripotent stem cells
- PMID: 33786455
- PMCID: PMC7988236
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2020.100213
An updated protocol for the cost-effective and weekend-free culture of human induced pluripotent stem cells
Abstract
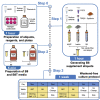
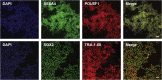
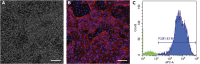
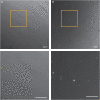
The protocol provided here describes methodologies for making a highly cost-effective, chemically defined medium for culturing hiPSCs we call B8 medium. The typical cost of B8 medium is US$10 per liter, which with modifications included here is more affordable than standard media. We provide simple protocols for making B8 supplement aliquots, making the basal media DMEM/F12, Matrigel-coated plates, thawing, passaging, culturing, and cryopreserving hiPSCs. We show typical differentiation results and provide a comprehensive troubleshooting guide. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Kuo et al. (2020).
Keywords: Cell Culture; Stem Cells.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Gao L., Nath S.C., Jiao X., Zhou R., Nishikawa S., Krawetz R., Li X., Rancourt D.E. Post-passage rock inhibition induces cytoskeletal aberrations and apoptosis in Human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Res. 2019;41:101641. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

