Matrine inhibits ovarian cancer cell viability and promotes apoptosis by regulating the ERK/JNK signaling pathway via p38MAPK
- PMID: 33786627
- PMCID: PMC8025149
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2021.8033
Matrine inhibits ovarian cancer cell viability and promotes apoptosis by regulating the ERK/JNK signaling pathway via p38MAPK
Retraction in
-
[Retracted] Matrine inhibits ovarian cancer cell viability and promotes apoptosis by regulating the ERK/JNK signaling pathway via p38MAPK.Oncol Rep. 2024 Aug;52(2):99. doi: 10.3892/or.2024.8758. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Oncol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38904204 Free PMC article.
Abstract
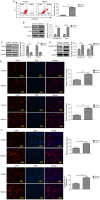
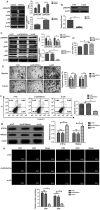
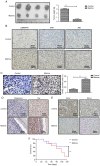
Ovarian cancer displays the highest mortality rate among all types of gynecological cancer worldwide. The survival of patients with ovarian cancer remains poor due to poor responses to anticancer treatments. The present study aimed to investigate the therapeutic effects and potential mechanism underlying matrine in ovarian cancer tissues, ovarian cancer cells and a CAOV‑3‑derived tumor‑bearing mouse model. MTT, migration, invasion, flow cytometry, immunofluorescence and immunohistochemistry assays were performed to assess the inhibitory effects of matrine on ovarian cancer. A xenograft ovarian cancer mouse model was established and treated with matrine or PBS. The results demonstrated that compared with the control group, matrine significantly induced ovarian cancer cell apoptosis by upregulating caspase‑8 and Fas cell surface death receptor (Fas) expression levels, and downregulating Bcl‑2 and Bcl‑xl expression levels. Moreover, compared with the control group, matrine significantly inhibited ovarian cancer cell viability, migration and invasion by downregulating metastasis associated protein‑1, fibronectin, angiotensin II type 2 receptor-interacting protein 3a and H high mobility group AT‑hook 2 expression levels. Compared with the control group, matrine significantly increased p38MAPK, phosphorylated (p)ERK/ERK and pJNK/JNK expression levels in ovarian cancer cells. p38MAPK knockdown significantly downregulated p38MAPK, pERK/ERK and pJNK/JNK expression levels compared with the control group, which significantly promoted ovarian cancer cell viability, migration and invasion. In vivo experiments demonstrated that compared with the control group, matrine significantly suppressed tumor growth by markedly upregulating p38MAPK, ERK and JNK expression levels. The immunohistochemistry results demonstrated that caspase‑8 and Fas expression levels were notably increased, whereas Bcl‑2 and Bcl‑xl expression levels were obviously decreased in matrine‑treated tumors compared with PBS‑treated tumors. In conclusion, the present study demonstrated that matrine inhibited ovarian cancer cell viability, migration and invasion, but induced cell apoptosis, suggesting that matrine may serve as a promising anticancer agent for the treatment of ovarian cancer.
Keywords: matrine; ovarian cancer; apoptosis; ERK/JNK signaling pathway; p38MAPK.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

