Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) and other autonomic disorders after COVID-19 infection: a case series of 20 patients
- PMID: 33786700
- PMCID: PMC8009458
- DOI: 10.1007/s12026-021-09185-5
Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) and other autonomic disorders after COVID-19 infection: a case series of 20 patients
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) and other autonomic disorders after COVID-19 infection: a case series of 20 patients.Immunol Res. 2021 Apr;69(2):212. doi: 10.1007/s12026-021-09191-7. Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 33851361 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: To describe clinical features, diagnostic findings, treatments, and outcomes in patients with new-onset postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) and other autonomic disorders following SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19).
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed medical records for patients who presented with persistent neurologic and cardiovascular complaints between April and December 2020 following COVID-19 infection.
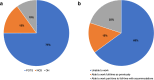
Results: Twenty patients (70% female) were included in this study.Fifteen had POTS, 3 had neurocardiogenic syncope, and 2 had orthostatic hypotension. Six patients had abnormalities on cardiac or pulmonary testing, and 4 had elevated autoimmune or inflammatory markers. All patients were treated with non-pharmacologic therapies, and most required pharmacologic therapies. Six to 8 months after COVID-19, 17 (85%) patients had residual autonomic symptoms, with 12 (60%) unable to return to work.
Conclusions: POTS can follow COVID-19 in previously healthy patients. Appropriate diagnostic investigations and therapies are necessary to identify and treat autonomic dysfunction after COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Neurocardiogenic syncope; Neurologic complications; Orthostatic hypotension; Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous