Physical exercise and prevention of falls. Effects of a Pilates training method compared with a general physical activity program: A randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 33787615
- PMCID: PMC8021317
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025289
Physical exercise and prevention of falls. Effects of a Pilates training method compared with a general physical activity program: A randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Introduction: Falls are the leading cause of injury-related mortality and morbidity in the elderly. Physical activity plays a key role in the prevention of falls and stimulates postural control. The aim of this study was to compare a general physical activity program for the elderly with a Pilates program to evaluate the effects on balance and on reducing the risk of falling.
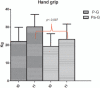
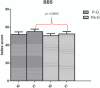
Materials and methods: Forty-six subjects were enrolled in this study, but only 41 were included in the study. The subjects were divided into 2 groups: Pilates group (P-G) and a group following a nonspecific program of physical activity (Pa-G). Each subject underwent the hand grip test, Berg balance scale test, and posturographic analysis.
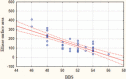
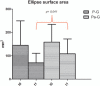
Results: Spearman correlation coefficient showed correlations between the following parameters: BBS versus hand grip test (r = 0.68); BBS versus ellipse surface area (r = -0.75). There were significant differences between groups after the exercise program: both groups showed an improvement in performance but the P-G recorded significantly better results than the Pa-G.
Discussion and conclusions: This study confirmed that physical activity improves both balance and strength. However, our data show that Pilates has a greater effect on these physical abilities than a general physical activity program.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Shryock HS, Siegel JS, Larmon EA. Census USBot The Methods and Materials of Demography U S Department of Commerce, Bureau of the Census 1980.
-
- Stenhagen M, Nordell E, Elmstahl S. Falls in elderly people: a multifactorial analysis of risk markers using data from the Swedish general population study ’Good ageing in Skane’. Aging Clin Exp Res 2013;25:59–67. - PubMed
-
- Patti A, Mammina C, Cataldo MC, et al. Relationship between hypertension and accidental falls: the potential positive effects of physical exercise on blood pressure. J Biol Res (Italy) 2015;88:113–4.
-
- Sturnieks DL, St George R, Lord SR. Balance disorders in the elderly. Neurophysiol Clin 2008;38:467–78. - PubMed
-
- Tuunainen E, Jantti P, Poe D, et al. Characterization of presbyequilibrium among institutionalized elderly persons. Auris Nasus Larynx 2012;39:577–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical