Estimated Costs and Long-term Outcomes of Patients With High-Risk Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Treated With Bacillus Calmette-Guérin in the Veterans Affairs Health System
- PMID: 33787908
- PMCID: PMC8013821
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.3800
Estimated Costs and Long-term Outcomes of Patients With High-Risk Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Treated With Bacillus Calmette-Guérin in the Veterans Affairs Health System
Abstract
Importance: Management of high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) represents a clinical challenge due to high failure rates despite prior bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) therapy.
Objective: To describe real-world patient characteristics, long-term outcomes, and the economic burden in a population with high-risk NMIBC treated with BCG therapy.
Design, setting, and participants: This retrospective cohort study identified 412 patients with high-risk NMIBC from 63 139 patients diagnosed with bladder cancer who received at least 1 dose of BCG within Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) centers across the US from January 1, 2000, to December 31, 2015. Adequate induction BCG therapy was defined as at least 5 installations, and adequate maintenance BCG therapy was defined as at least 7 installations. Data were analyzed from January 2, 2020, to January 20, 2021.
Exposures: Intravesical BCG therapy, including adequate induction BCG therapy, was defined as at least 5 intravesical instillations of BCG within 70 days from BCG therapy start date. Adequate maintenance BCG therapy was defined as at least 7 installations of BCG within 274 days of the start (the first instillation) of adequate induction BCG therapy (ie, adequate induction BCG plus some form of additional BCG).
Main outcomes and measures: The Kaplan-Meier method was used to estimate outcomes, including event-free survival. All-cause expenditures were summarized as medians with corresponding interquartile ranges (IQRs) and adjusted to 2019 USD.
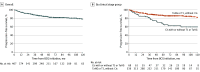
Results: Of the 412 patients who met inclusion criteria, 335 (81%) were male and 77 (19%) were female, with a median age of 67 (IQR, 61-74) years. Follow-up was 2694 person-years. A total of 392 patients (95%) received adequate induction BCG therapy, and 152 (37%) received adequate BCG therapy. For all patients with high-risk NMIBC, the 10-year progression-free survival rate and disease-specific death rate were 78% and 92%, respectively. Patients with carcinoma in situ (Cis) had worse disease-free survival than those without Cis (hazard ratio [HR], 1.85; 95% CI, 1.34-2.56). Total median costs at 1 year were $29 459 (IQR, $14 991-$52 060); at 2 years, $55 267 (IQR, $28 667-$99 846); and at 5 years, $117 361 (IQR, $59 680-$211 298). Patients with progressive disease had significantly higher median 5-year costs ($232 729 [IQR, $151 321-$341 195] vs $94 879 [IQR, $52 498-$172 631]; P < .001), with outpatient care, pharmacy, and surgery-related costs contributing.
Conclusions and relevance: Despite adequate induction BCG therapy, only 37% of patients received adequate BCG therapy. Patients with Cis had increased risk of progression, and progression regardless of Cis was associated with significantly increased costs relative to patients without progression. Extrapolating cost figures, regardless of progression, resulted in nationwide costs at 1 year of $373 million for patients diagnosed with high-risk NMIBC in 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Quantifying the Costs of Care Among Patients With High-Risk Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Treated in the Veterans Health Administration.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Mar 1;4(3):e213816. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.3816. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 33787916 No abstract available.
-
Urological Oncology: Bladder, Penis and Urethral Cancer, and Basic Principles of Oncology.J Urol. 2022 May;207(5):1153-1155. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000002460. Epub 2022 Feb 10. J Urol. 2022. PMID: 35139651 No abstract available.
References
-
- Scher H, Bahnson R, Cohen S, et al. ; National Comprehensive Cancer Network . NCCN urothelial cancer practice guidelines. Oncology (Williston Park). 1998;12(7A):225-271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

