Variation in propofol induction doses administered to surgical patients over age 65
- PMID: 33788251
- PMCID: PMC8373684
- DOI: 10.1111/jgs.17139
Variation in propofol induction doses administered to surgical patients over age 65
Abstract
Background/objectives: Advanced age is associated with increased susceptibility to acute adverse effects of propofol. The present study aimed to describe patterns of propofol dosing for induction of general anesthesia before endotracheal intubation in a nationwide sample of older adults presenting for surgery.
Design: Retrospective observational study using the Multicenter Perioperative Outcomes Group data set.
Setting: Thirty-six institutions across the United States.
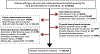
Participants: A total of 350,766 patients aged over 65 years who received propofol for general anesthetic induction and endotracheal intubation between 2014 and 2018.
Intervention: None.
Measurements: Total induction bolus dose of propofol administered.
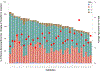
Results: The mean (SD) weight-adjusted propofol dose was 1.7 (0.6) mg/kg. The mean prevalent propofol induction dose exceeded the upper bound of what has been described as the typical geriatric dose requirement across every age category examined. The percent of patients receiving propofol induction doses above the described typical geriatric range was 64.8% (95% CI 64.6-65.0), varying from 73.8% among patients aged 65-69 to 45.8% among patients aged 80 and older.
Conclusion: The present study of a large multicenter cohort demonstrates that prevalent propofol dosing commonly falls above the published typically required dose range for patients aged ≥65 in nationwide anesthetic practice. Widespread variability in induction dose administration remains incompletely explained by known patient variables. The nature and clinical consequences of these unexplained dosing decisions remain important topics for further study. Observed discordance between expected and actual induction dosing raises the question of whether there should be reconsideration of widespread provider practice or, alternatively, whether what is published as the typical propofol induction dose range should be revisited.
Keywords: anesthetic induction; geriatric dosing; propofol.
© 2021 The American Geriatrics Society.
Figures

Comment in
-
Goldilocks and propofol dosage in older adults: Too much, too little, or just right?J Am Geriatr Soc. 2021 Aug;69(8):2106-2109. doi: 10.1111/jgs.17221. Epub 2021 May 8. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2021. PMID: 33964173 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Comment on: Variation in propofol induction doses administered to surgical patients over age 65.J Am Geriatr Soc. 2021 Sep;69(9):2678-2679. doi: 10.1111/jgs.17328. Epub 2021 Jun 29. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2021. PMID: 34185880 No abstract available.
-
Reply to: Comment on: Variation in propofol induction doses administered to surgical patients over 65.J Am Geriatr Soc. 2021 Sep;69(9):2680-2681. doi: 10.1111/jgs.17327. Epub 2021 Jun 29. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2021. PMID: 34185888 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- United States Census Bureau; Quick Facts - Persons 65 years and over, percent; url: https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/US/AGE775219 as accessed June 25, 2020.
-
- Popovic JR. 1999 National Hospital Discharge Survey: annual summary with detailed diagnosis and procedure data. Vital Health Stat 13. 2001;2001September;(151):i–v. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

