Escherichia coli RNase E can efficiently replace RNase Y in Bacillus subtilis
- PMID: 33788929
- PMCID: PMC8096251
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkab216
Escherichia coli RNase E can efficiently replace RNase Y in Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
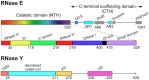
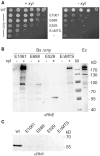
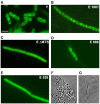
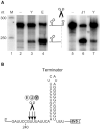
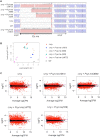
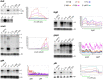
RNase Y and RNase E are disparate endoribonucleases that govern global mRNA turnover/processing in the two evolutionary distant bacteria Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli, respectively. The two enzymes share a similar in vitro cleavage specificity and subcellular localization. To evaluate the potential equivalence in biological function between the two enzymes in vivo we analyzed whether and to what extent RNase E is able to replace RNase Y in B. subtilis. Full-length RNase E almost completely restores wild type growth of the rny mutant. This is matched by a surprising reversal of transcript profiles both of individual genes and on a genome-wide scale. The single most important parameter to efficient complementation is the requirement for RNase E to localize to the inner membrane while truncation of the C-terminal sequences corresponding to the degradosome scaffold has only a minor effect. We also compared the in vitro cleavage activity for the major decay initiating ribonucleases Y, E and J and show that no conclusions can be drawn with respect to their activity in vivo. Our data confirm the notion that RNase Y and RNase E have evolved through convergent evolution towards a low specificity endonuclease activity universally important in bacteria.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
References
-
- Apirion D., Lassar A.B.. A conditional lethal mutant of Escherichia coli which affects processing of ribosomal RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 1978; 253:1738–1742. - PubMed
-
- Ono M., Kuwano M.. A conditional lethal mutation in an E. coli strain with a longer chemical lifetime of messenger RNA. J. Mol. Biol. 1979; 129:343–357. - PubMed
-
- Carpousis A.J., Van Houwe G., Ehretsmann C., Krisch H.M.. Copurification of E. coli RNAse E and PNPase: evidence for a specific association between two enzymes important in mRNA processing and degradaion. Cell. 1994; 76:889–900. - PubMed
-
- Py B., Higgins C.F., Krisch H.M., Carpousis A.J.. A DEAD-box RNA helicase in the Escherichia coli RNA degradosome. Nature. 1996; 381:169–172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

