Comparative Renal Effects of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors on Individual Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 33789035
- PMCID: PMC8090474
- DOI: 10.3803/EnM.2020.912
Comparative Renal Effects of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors on Individual Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: To compare the renal effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors and sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors on individual outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods: We searched electronic databases (MEDLINE, Embase, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials) from inception to June 2019 to identity eligible randomized controlled trials of DPP-4 inhibitors or SGLT2 inhibitors that reported at least one kidney outcome in patients with type 2 diabetes. Outcomes of interest were microalbuminuria, macroalbuminuria, worsening nephropathy, and end-stage kidney disease (ESKD). We performed an arm-based network meta-analysis using Bayesian methods and calculated absolute risks and rank probabilities of each treatment for the outcomes.
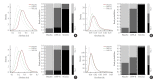
Results: Seventeen studies with 87,263 patients were included. SGLT2 inhibitors significantly lowered the risks of individual kidney outcomes, including microalbuminuria (odds ratio [OR], 0.64; 95% credible interval [CrI], 0.41 to 0.93), macroalbuminuria (OR, 0.48; 95% CrI, 0.24 to 0.72), worsening nephropathy (OR, 0.65; 95% CrI, 0.44 to 0.91), and ESKD (OR, 0.65; 95% CrI, 0.46 to 0.98) as compared with placebo. However, DPP-4 inhibitors did not lower the risks. SGLT2 inhibitors were considerably associated with higher absolute risk reductions in all kidney outcomes than DPP-4 inhibitors, although the benefits were statistically insignificant. The rank probabilities showed that SGLT2 inhibitors were better treatments for lowering the risk of albuminuria and ESKD than placebo or DPP-4 inhibitors.
Conclusion: SGLT2 inhibitors were superior to DPP-4 inhibitors in reducing the risk of albuminuria and ESKD in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: Albuminuria; Diabetes mellitus, type 2; Diabetic nephropathies; Dipeptidyl-peptidase IV inhibitors; Kidney failure, chronic; Network meta-analysis; Sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Comment in
-
New Era for Renal-Protective Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes: Better Renal Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Taking Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors versus Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors.Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2021 Apr;36(2):339-341. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2021.203. Epub 2021 Apr 27. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2021. PMID: 33934589 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Webster AC, Nagler EV, Morton RL, Masson P. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet. 2017;389:1238–52. - PubMed
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF diabetes atlas. 9th ed. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation; 2019.
-
- Tonelli M, Wiebe N, Culleton B, House A, Rabbat C, Fok M, et al. Chronic kidney disease and mortality risk: a systematic review. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:2034–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

