Effect of dural inflammatory soup application on activation and sensitization markers in the caudal trigeminal nucleus of the rat and the modulatory effects of sumatriptan and kynurenic acid
- PMID: 33789568
- PMCID: PMC8011387
- DOI: 10.1186/s10194-021-01229-3
Effect of dural inflammatory soup application on activation and sensitization markers in the caudal trigeminal nucleus of the rat and the modulatory effects of sumatriptan and kynurenic acid
Abstract
Background: The topical inflammatory soup can model the inflammation of the dura mater causing hypersensitivity and activation of the trigeminal system, a phenomenon present in migraineurs. Calcitonin gene-related peptide, transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 receptor, and neuronal nitric oxide synthase are important in the sensitization process there. 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonists, triptans are used as a treatment of migraine. Kynurenic acid an NMDA antagonist can act on structures involved in trigeminal activation.
Aim: We investigated the effect of inflammatory soup induced dural inflammation on the calcitonin gene-related peptide, transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 receptor, and neuronal nitric oxide synthase levels in the caudal trigeminal nucleus. We also tested whether pretreatment with a well-known antimigraine drug, such as sumatriptan and kynurenic acid, a compound with a different mechanism of action, can affect these changes and if their modulatory effects are comparable.
Material and methods: After subcutaneous sumatriptan or intraperitoneal kynurenic acid the dura mater of adult male Sprague-Dawley rats (n = 72) was treated with inflammatory soup or its vehicle (synthetic interstitial fluid). Two and a half or four hours later perfusion was performed and the caudal trigeminal nucleus was removed for immunohistochemistry.
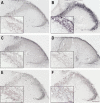
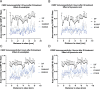
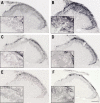
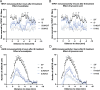
Results and conclusion: Inflammatory soup increased calcitonin gene-related peptide, transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 receptor, and neuronal nitric oxide synthase in the caudal trigeminal nucleus compared to placebo, which was attenuated by sumatriptan and kynurenic acid. This suggests the involvement of 5-HT1B/1D and NMDA receptors in neurogenic inflammation development of the dura and thus in migraine attacks.
Keywords: CGRP; Inflammatory soup; Kynurenic acid; Migraine; Sumatriptan; TRPV1; Trigeminal system; nNOS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest concerning the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

