Harnessing machine learning to guide phylogenetic-tree search algorithms
- PMID: 33790270
- PMCID: PMC8012635
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-22073-8
Harnessing machine learning to guide phylogenetic-tree search algorithms
Abstract
Inferring a phylogenetic tree is a fundamental challenge in evolutionary studies. Current paradigms for phylogenetic tree reconstruction rely on performing costly likelihood optimizations. With the aim of making tree inference feasible for problems involving more than a handful of sequences, inference under the maximum-likelihood paradigm integrates heuristic approaches to evaluate only a subset of all potential trees. Consequently, existing methods suffer from the known tradeoff between accuracy and running time. In this proof-of-concept study, we train a machine-learning algorithm over an extensive cohort of empirical data to predict the neighboring trees that increase the likelihood, without actually computing their likelihood. This provides means to safely discard a large set of the search space, thus potentially accelerating heuristic tree searches without losing accuracy. Our analyses suggest that machine learning can guide tree-search methodologies towards the most promising candidate trees.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
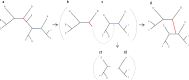
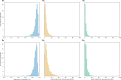
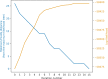
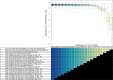
References
-
- Saitou N, Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987;4:406–425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

