Tocilizumab: An Effective Therapy for Severely and Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients
- PMID: 33790504
- PMCID: PMC7991771
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-23747
Tocilizumab: An Effective Therapy for Severely and Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
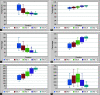
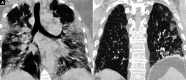
Background: Tocilizumab (TCZ), a monoclonal antibody against the most prevalent cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6), is an emerging therapeutic option for COVID-19 infections. The present study was undertaken to assess the therapeutic response of TCZ therapy in severely or critically ill COVID-19 patients and its role as an effective modality of management. Methods: The present retrospective observational study included 30 admitted severely or critically ill COVID-19 patients, treated with TCZ therapy on behalf of raised IL-6 levels. The patients' data concerning medical history, clinical manifestation, arterial blood gas analysis, mode of oxygenation, radiological imaging, and outcome were extracted from their medical records and compared pre- and post-TCZ infusion. Results: All patients of the study group had symptomatic presentations with a mean PaO2/FiO2 (P/F) ratio of 205.41 before TCZ infusion. All patients had a raised IL-6 level (mean value 206.56 pg/mL) that was extremely elevated in 90% of patients. Infusion of TCZ dramatically reduced mean body temperature (100.78-99.32°F) and the requirement for supplemental oxygen (68-48%) and improved mean SpO2 (86-89%) and mean P/F ratio (208-240) within 24 hours. Three patients on noninvasive ventilation were weaned off after TCZ infusion. Serum levels of IL-6 were raised initially but declined within 3-5 days of post-TCZ infusion. Conclusion: TCZ appears to be an effective therapeutic option in severely or critically ill COVID-19 patients with raised IL-6 levels. TCZ immediately improves the clinical status of patients by a probable mechanism of inhibition of cytokine storm and reduces COVID-19-related mortalities. How to cite this article: Bhandari S, Rankawat G, Singh A. Tocilizumab: An Effective Therapy for Severely and Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. Indian J Crit Care Med 2021;25(3):260-266.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cytokine storm; Interleukin-6; Tocilizumab.
Copyright © 2021; Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None
Figures
References
-
- Hui DS, Azhar EI, Madani TA, Ntoumi F, Kock R, Dar O et al. The continuing 2019-nCoV epidemic threat of novel coronaviruses to global health—the latest 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China. Int J Infect Dis. 2020;;91::264––266.. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.01.009. DOI: . PMC 7128332. PMID 31953166. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lan J, Ge JW, Yu JF, Shan SS, Zhou H, Fan SL et al. Crystal structure of the 2019-nCoV spike receptor-binding domain bound with the ACE2 receptor. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.02.19.956235v1. 2020. doi: 10.1101/2020.02.19.956235. Available from: DOI: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
