Urinary Metabolite Signatures for Predicting Elderly Stroke Survivors with Depression
- PMID: 33790561
- PMCID: PMC8007561
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S299835
Urinary Metabolite Signatures for Predicting Elderly Stroke Survivors with Depression
Abstract
Background: Post-stroke depression (PSD) is a major complication in stroke survivors, especially in elderly stroke survivors. But there are still no objective methods to diagnose depression in elderly stroke survivors. Thus, this study was conducted to identify potential biomarkers for diagnosing elderly PSD subjects.
Methods: Elderly (60 years or older) stroke survivors with depression were assigned into the PSD group, and elderly stroke survivors without depression and elderly healthy controls (HCs) were assigned into the non-depressed group. Urinary metabolite signatures obtained from gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS)-based metabolomic platform were collected. Both univariate and multivariate statistical analysis were used to find the differential urinary metabolites between the two groups.
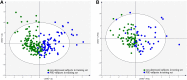
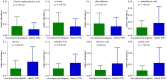
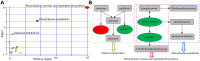
Results: The 78 elderly HCs, 122 elderly stroke survivors without depression and 124 elderly PSD subjects were included. A set of 13 differential urinary metabolites responsible for distinguishing PSD subjects from non-depressed subjects were found. The Phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis, Phenylalanine metabolism and Galactose metabolism were found to be significantly changed in elderly PSD subjects. The phenylalanine was significantly negatively correlated with age and depressive symptoms. Meanwhile, a biomarker panel consisting of 3-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, tyrosine, phenylalanine, sucrose, palmitic acid, glyceric acid, azelaic acid and α-aminobutyric acid was identified.
Conclusion: These results provided candidate molecules for developing objective methods to diagnose depression in elderly stroke survivors, suggested that taking supplements of phenylalanine might be an effective method to prevent depression in elderly stroke survivors, and would be helpful for future revealing the pathophysiological mechanism of PSD.
Keywords: biomarker; metabolomics; post-stroke depression.
© 2021 Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial or other conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of Potential Metabolite Markers for Middle-Aged Patients with Post-Stroke Depression Using Urine Metabolomics.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2020 Aug 25;16:2017-2024. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S271990. eCollection 2020. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2020. PMID: 32922015 Free PMC article.
-
Does urinary metabolite signature act as a biomarker of post-stroke depression?Front Psychiatry. 2022 Aug 24;13:928076. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.928076. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36090365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Urinary Metabolite Signature for Non-invasive Post-stroke Depression Diagnosis.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015 Jul;72(3):661-7. doi: 10.1007/s12013-014-0472-9. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015. PMID: 27352185
-
Urinary biomarkers for diagnosing poststroke depression in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2019 Aug 13;12:1379-1386. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S215187. eCollection 2019. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2019. PMID: 31496775 Free PMC article.
-
The advances of post-stroke depression: 2021 update.J Neurol. 2022 Mar;269(3):1236-1249. doi: 10.1007/s00415-021-10597-4. Epub 2021 May 30. J Neurol. 2022. PMID: 34052887 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Progress in Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics in Major Depressive Disorder Research.Molecules. 2023 Nov 4;28(21):7430. doi: 10.3390/molecules28217430. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37959849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling Metabolic Changes following Stroke: Insights from a Urinary Metabolomics Analysis.Metabolites. 2024 Feb 28;14(3):145. doi: 10.3390/metabo14030145. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 38535305 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics reveals key biomarkers for ischemic stroke: a systematic review of emerging evidence.Front Neurol. 2025 Aug 8;16:1630390. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1630390. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40860967 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of continuous intravenous infusion with propofol on intestinal metabolites in rats.Biomed Rep. 2023 Dec 20;20(2):25. doi: 10.3892/br.2023.1713. eCollection 2024 Feb. Biomed Rep. 2023. PMID: 38169795 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Electroacupuncture on Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolites in Rats with Poststroke Depression.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2023 Jul 12;19:1581-1592. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S415098. eCollection 2023. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2023. PMID: 37465562 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

