Development of Dermatitis Herpetiformis in Chronic Plaque Psoriasis
- PMID: 33790758
- PMCID: PMC7989782
- DOI: 10.1159/000512870
Development of Dermatitis Herpetiformis in Chronic Plaque Psoriasis
Abstract
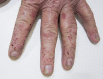
Chronic plaque psoriasis is often associated with autoimmune bullous diseases. Dermatitis herpetiformis (DH) is a rare immunobullous disease that has been linked to celiac disease (CD). To our knowledge, the coexistence of psoriasis and DH is uncommon, and has only been described in anecdotal reports. We report a case of chronic plaque psoriasis complicated by DH in a 60-year-old patient with no known history of CD or associated symptoms. In our patient, DH presented atypically as multiple vesicles along the edges of psoriatic plaques located on the back and hips, and as vesiculobullous eruptions on the fingers. The patient was successfully treated with a combination of dapsone and a gluten-free diet for DH, and secukinumab for psoriasis. This case highlights the importance of screening for CD in patients with psoriasis, as well as other concomitant autoimmune diseases. A gluten-free diet should be trialled in psoriatic patients with positive CD serology.
Keywords: Celiac disease; Dermatitis herpetiformis; Psoriasis.
Copyright © 2021 by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare with respect to the research and/or authorship of this case report.
Figures


References
-
- Agusti-Mejias A, Messeguer F, García-Ruiz R, de Unamuno B, Pérez-Ferriols A, Sánchez-Carazo JL, et al. [Concomitant dermatitis herpetiformis and plaque psoriasis: possible skin manifestations of celiac disease] Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2011 Jul-Aug;102((6)):471–3. - PubMed
-
- Gkalpakiotis S, Arenberger P, Sticova E, Sefrnova P, Arenbergerova M. Long-term combination therapy of ustekinumab and dapsone in a patient with psoriasis and dermatitis herpetiformis Duhring. J Dermatol. 2012 Dec;39((12)):1074–5. - PubMed
-
- Aytekin S, Inalöz HS, Harman M, Akdeniz S, Deveci E, Inalöz SS. Coexistence of psoriasis vulgaris and bullous disorders. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 1999 Mar;12((2)):185–7. - PubMed
-
- Acharya P, Mathur M. Association between psoriasis and celiac disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jun;82((6)):1376–85. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

