Long-Term Remission with Ipilimumab/Nivolumab in Two Patients with Different Soft Tissue Sarcoma Subtypes and No PD-L1 Expression
- PMID: 33790767
- PMCID: PMC7991270
- DOI: 10.1159/000512828
Long-Term Remission with Ipilimumab/Nivolumab in Two Patients with Different Soft Tissue Sarcoma Subtypes and No PD-L1 Expression
Abstract
Checkpoint inhibitor therapy has been shown to improve outcomes in multiple solid malignancies; however, data are limited in soft tissue sarcoma. We present two cases of patients with advanced soft tissue sarcoma of different subtypes (dedifferentiated liposarcoma and myxofibrosarcoma) with zero percent PD-L1 expression by immunohistochemistry who were treated with ipilimumab and nivolumab followed by maintenance nivolumab. Both patients had failed multiple lines of systemic treatment and experienced long-term remission after starting ipilimumab and nivolumab. Genetic testing revealed that no genetic mutations were found in common between the two cases. One patient received concurrent cryoablation, which may have sensitized his tumor to immunotherapy. Checkpoint inhibitor therapy may improve outcomes in soft tissue sarcoma regardless of PD-L1 status, especially when combined with cryoablation. Studies are needed to evaluate whether treatment response varies by sarcoma subtype and what molecular markers can be used to guide patient selection.
Keywords: Ipilimumab; Nivolumab; PD-1 blockade; PD-L1 status; Sarcoma.
Copyright © 2021 by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
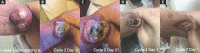
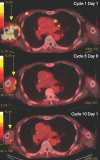
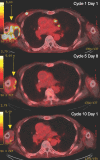
References
-
- Herbst RS, Baas P, Kim DW, Felip E, Pérez-Gracia JL, Han JY, et al. Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;387((10027)):1540–50. - PubMed
-
- Plimack ER, Bellmunt J, Gupta S, Berger R, Chow LQ, Juco J, et al. Safety and activity of pembrolizumab in patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer (KEYNOTE-012): a non-randomised, open-label, phase 1b study. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18((2)):212–20. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

