PPE-associated dermatoses: effect on work and wellbeing
- PMID: 33791479
- PMCID: PMC8004352
- DOI: 10.7861/fhj.2020-0210
PPE-associated dermatoses: effect on work and wellbeing
Abstract
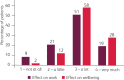
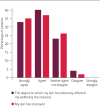
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to more stringent infection control practice within hospitals, with the added requirement of personal protective equipment (PPE). Consequentially, the incidence of PPE-related dermatoses in healthcare workers is increasing. Analysis of staff members seen in a dermatology self-referral service during the first COVID-19 peak revealed a wide range of healthcare professionals being affected, with irritant hand dermatitis and acneiform eruptions being the commonest diagnoses. These PPE-related dermatoses had significant effects on staff members' work and wellbeing, which improved following assessment and treatment by dermatology. Given the change to our behaviour wearing PPE daily, which is likely to continue for the foreseeable future, the consequences will inevitably affect both healthcare workers and the general public, with these common dermatoses presenting in both primary and secondary care. It is therefore imperative to recognise both the physical and emotional impact that COVID-19 PPE has, and initiate prompt treatment to improve wellbeing.
Keywords: PPE; dermatology; hand dermatitis; occupational dermatoses; wellbeing.
© Royal College of Physicians 2021. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Cvetkovski RS, Zachariae R, Jensen H, Olsen J, Johansen JD, Agner T. Quality of life and depression in a population of occupational hand eczema patients. Contact Dermatitis 2006;54:106–11. - PubMed
-
- Smedley J, Williams S, Peel P, Pedersen K. Management of occupational dermatitis in healthcare workers: a systematic review. Occup Environ Med 2012;69:276–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources