Ccr4-Not as a mediator of environmental signaling: a jack of all trades and master of all
- PMID: 33791857
- PMCID: PMC8405566
- DOI: 10.1007/s00294-021-01180-5
Ccr4-Not as a mediator of environmental signaling: a jack of all trades and master of all
Abstract
The cellular response to environmental exposures, such as nutrient shifts and various forms of stress, requires the integration of the signaling apparatus that senses these environmental changes with the downstream gene regulatory machinery. Delineating this molecular circuitry remains essential for understanding how organisms adapt to environmental flux, and it is critical for determining how dysregulation of these mechanisms causes disease. Ccr4-Not is a highly conserved regulatory complex that controls all aspects of the gene expression process. Recent studies in budding yeast have identified novel roles for Ccr4-Not as a key regulator of core nutrient signaling pathways that control cell growth and proliferation, including signaling through the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (TORC1) pathway. Herein, I will review the current evidence that implicate Ccr4-Not in nutrient signaling regulation, and I will discuss important unanswered questions that should help guide future efforts to delineate Ccr4-Not's role in linking environmental signaling with the gene regulatory machinery. Ccr4-Not is highly conserved throughout eukaryotes, and increasing evidence indicates it is dysregulated in a variety of diseases. Determining how Ccr4-Not regulates these signaling pathways in model organisms such as yeast will provide a guide for defining how it controls these processes in human cells.
Keywords: Ccr4-Not; Lysosome; Nutrient signaling; TORC1; Transcription; V-ATPase.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
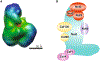
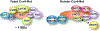
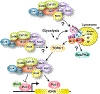
References
-
- Butow RA, Avadhani NG (2004) Mitochondrial signaling: the retrograde response. Mol Cell 14 (1):1–15 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

