Antimicrobial Nano-Agents: The Copper Age
- PMID: 33792292
- PMCID: PMC8155324
- DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.0c10756
Antimicrobial Nano-Agents: The Copper Age
Abstract
The constant advent of major health threats such as antibacterial resistance or highly communicable viruses, together with a declining antimicrobial discovery, urgently requires the exploration of innovative therapeutic approaches. Nowadays, strategies based on metal nanoparticle technology have demonstrated interesting outcomes due to their intrinsic features. In this scenario, there is an emerging and growing interest in copper-based nanoparticles (CuNPs). Indeed, in their pure metallic form, as oxides, or in combination with sulfur, CuNPs have peculiar behaviors that result in effective antimicrobial activity associated with the stimulation of essential body functions. Here, we present a critical review on the state of the art regarding the in vitro and in vivo evaluations of the antimicrobial activity of CuNPs together with absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (ADMET) assessments. Considering the potentiality of CuNPs in antimicrobial treatments, within this Review we encounter the need to summarize the behaviors of CuNPs and provide the expected perspectives on their contributions to infectious and communicable disease management.
Keywords: ADMET; antimicrobials; antiviral; bacteria; biodistribution; communicable diseases; copper; nanoparticles; virus; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


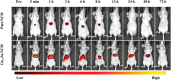
References
-
- Akhavan O.; Ghaderi E. Cu and CuO Nanoparticles Immobilized by Silica Thin Films as Antibacterial Materials and Photocatalysts. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 205 (1), 219–223. 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2010.06.036. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

